- 1. Why This Judgment?
- 2. Three Core Factors Affecting “Suitability for High-Pressure Applications”
- 3. Concise Comparison Table (A53 / A106 / API-5L)
- 4. Practical Engineering Steps: How to Determine “Whether a Specific A53 Pipeline Can Withstand Pressure”?
- 5. Practical Recommendations
- 6. LONGMA — How We Can Assist You
- 7. References & Basis (Excerpts)
ASTM A53 is generally not recommended as the first choice for “high-pressure, safety-critical” pipelines. It is suitable for low to medium-pressure applications involving steam, water, gas, and structural uses. When the design pressure/temperature is extremely high, or strict requirements are imposed on weld integrity and long-term corrosion resistance, priority should be given to seamless A106, API-5L, or alloy materials, with verification through ASME design calculations.
Why This Judgment?
-
- Standard Scope: ASTM A53 covers seamless and welded black pipes/hot-dip galvanized pipes, with nominal sizes ranging from NPS 1/8 to 26. Its specification states that ASTM A53 provides general-purpose piping for mechanical and pressure applications, but it does not position “high-pressure, high-temperature critical transmission” as a priority.
- Mechanical Properties: ASTM A53 specifies minimum yield and tensile strength requirements for Grade A and Grade B (representative values: Grade A has a yield strength of approximately 205 MPa and a tensile strength of approximately 330 MPa; Grade B has a yield strength of approximately 240 MPa and a tensile strength of approximately 415 MPa). These values determine the basic pressure-bearing capacity of the pipe.
- Industry Practice: Industry documents and suppliers generally classify ASTM A53 as suitable for “low/medium-pressure” and structural applications. For pipeline projects involving long-term operation under high pressure or high temperature, ASTM A106 (seamless, for high-temperature use) or API 5L (pipeline transmission specification) are more commonly selected.
Three Core Factors Affecting “Suitability for High-Pressure Applications”
-
- Material and Grade— Higher yield/tensile strength allows for higher design pressure; ASTM A53 Grade B outperforms Grade A.
- Wall Thickness (Schedule) and Diameter— For the same material, a thicker wall and smaller diameter result in higher pressure-bearing capacity (calculable using Barlow’s Formula or the thickness formula in ASME B31.3). The design must include calculation of the allowable pressure in accordance with ASME pipeline formulas.
- Weld and Manufacturing Quality (ERW vs. Seamless)— For ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) pipes of Grade B, welds typically require heat treatment (≥1000°F/≈540°C) and must undergo NDE (Non-Destructive Examination)/hydrostatic testing. High-pressure critical pipelines often favor seamless pipes or demand more stringent weld inspection (100% radiography or ultrasonic testing (UT)).
Concise Comparison Table (A53 / A106 / API-5L)
| Item | ASTM A53 (ERW/Seamless) | ASTM A106 (Seamless) | API-5L (Transmission Pipe) |
| Manufacturing Process | ERW or Seamless | Seamless only | Seamless or welded (classified into PSL1/PSL2) |
| Typical Applications | Low–medium pressure, structural, water supply/drainage | High-temperature / pressure pipelines | Oil and gas transmission, long-distance high-pressure lines |
| Representative Strength | Grade B: Yield ≈240 MPa, Tensile ≈415 MPa | Similar or more stringent seamless specifications (suitable for high temperatures) | Covers higher strength and inspection requirements depending on the grade |
| Weld/Inspection | ERW welds require heat treatment & NDE | No welds (lower weld-related risks) | PSL2 may require more stringent inspection (100% radiography) |
| Suitability for “High-Pressure Critical Applications” | Suitable for medium pressure after design verification; not the first choice for high-pressure critical applications | More suitable for high-temperature/high-pressure applications | Commonly used for high-pressure oil and gas transmission; suitable for critical lines when following PSL2/100% RT |
Data and application differentiations are referenced from ASTM standards and industry documentation.
Practical Engineering Steps: How to Determine “Whether a Specific A53 Pipeline Can Withstand Pressure”?
- Clarify design conditions: design pressure (gauge pressure), temperature, medium type, and allowable corrosion margin.
- Use ASME B31.3 / Barlow’s Formula to calculate the allowable pressure or required minimum wall thickness based on the material’s allowable stress (S), diameter (D), and candidate wall thickness (t).
- Review the Material Test Certificate (MTC): verify chemical composition, mechanical test results, and heat treatment records.
- For ERW products: request weld heat treatment records (A53 Grade B ≥540°C)and weld NDE (UT/RT)/hydrostatic test certification.
- For pipelines involving “continuous operation with high pressure/high temperature/hazardous media”, prioritize switching to seamless A106 or API-5L (PSL2) and require more stringent inspection.
Practical Recommendations
- If your design pressure falls within the “conventional low to medium range” (satisfiable via Barlow/ASME calculations) and you can strictly enforce requirements for wall thickness, weld heat treatment + NDE + hydrostatic testing, ASTM A53 (especially Grade B) can be used. However, for long-term high-pressure/high-temperature or safety-critical pipelines, priority should be given to seamless A106 or API-5L, with design and 100% necessary inspection conducted in accordance with relevant codes.
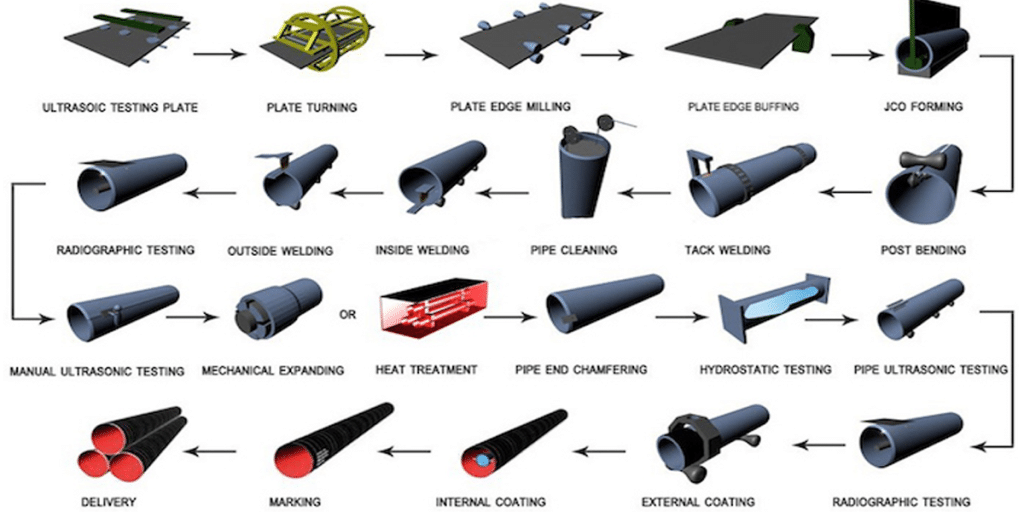
LONGMA — How We Can Assist You
We are LONGMA, specialized in ERW and LSAW round pipe production for over 20 years:
- We supply pipes in accordance with ASTM A53 / A106 / API-5L (ERW and LSAW) and provide complete MTCs, weld heat treatment records, NDE/RT/UT reports, and hydrostatic pressure curves.
- For high-pressure/high-temperature or safety-critical projects, we can assist with ASME B31.3 pressure verification, wall thickness selection, recommendations for alternative materials (A106/API), and provide sample pipes and test samples.
- We maintain stable production capacity and trackable lead times, and support customized anti-corrosion treatment and end processing (flange/threaded/grooved).
Want to confirm whether ASTM A53 is suitable for your specific pipeline? Send us your design pressure, temperature, pipe diameter, and medium. We will provide feasibility conclusions and cost-effective alternative solutions based on ASME calculations, along with a preliminary quotation and technical recommendations within 48 hours.
References & Basis (Excerpts)
ASTM A53 Standard Specifications; ASTM A53 Mechanical Property Tables; Industry Material Comparisons (A53 vs A106); ERW Weld Heat Treatment and Inspection Requirements; ASME B31.3 / Barlow Calculation Formulas.