- 1. Detailed Definition and Applications of ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
- 2. Manufacturing Process and Quality Control Differences between ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
- 3. Performance Comparison of ASTM A671 vs ASTM A672
- 4. Detailed introduction of ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
- 5. How to Correctly Choose ASTM A671 or ASTM A672 Steel Pipes in a Project?
In the fields of industrial manufacturing and pipeline engineering, the selection of welded steel pipes directly impacts the safety and service life of projects. Among the numerous welded steel pipe standards, ASTM A671 and ASTM A672 are particularly important industrial welded pipeline standards. Many engineers and procurement professionals often feel confused when comparing ASTM A671 vs A672, uncertain about how to make the most reasonable choice based on specific needs. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the performance comparison between A671 and A672 from aspects such as welded steel pipe heat treatment standards and performance indicators, helping you grasp the key points of pressure pipeline steel pipe selection to ensure both project quality and economic efficiency.
Detailed Definition and Applications of ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
1. Definition of ASTM A671
ASTM A671 is a standard specification for carbon and low-alloy steel welded pipes used in pressure applications. It primarily covers pipes designed for high-temperature and high-pressure pipeline systems. This standard specifies chemical composition, mechanical properties, manufacturing processes, and welding quality requirements to ensure excellent strength and corrosion resistance in harsh industrial environments.
2. Definition of ASTM A672
ASTM A672 mainly applies to large-diameter, thick-wall welded steel pipes for structural purposes. It is suitable for industrial pipelines and structural components subjected to heavy mechanical stress. This standard emphasizes structural strength and dimensional stability, often involving welded steel pipe heat treatment standards to enhance overall performance.
3. Comparison of Applications
ASTM A671 is mainly used for pressure pipeline systems requiring high-temperature and corrosion resistance, such as boiler tubes and chemical process piping.
ASTM A672 focuses more on structural uses, suitable for bridges, building frameworks, and large machinery piping structures where load-bearing and pressure resistance are critical.
4. Performance Differences: ASTM A671 generally requires stricter chemical composition control and heat treatment processes to ensure stability under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. ASTM A672 emphasizes thick-wall, large-diameter pipe dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties to meet structural application needs.
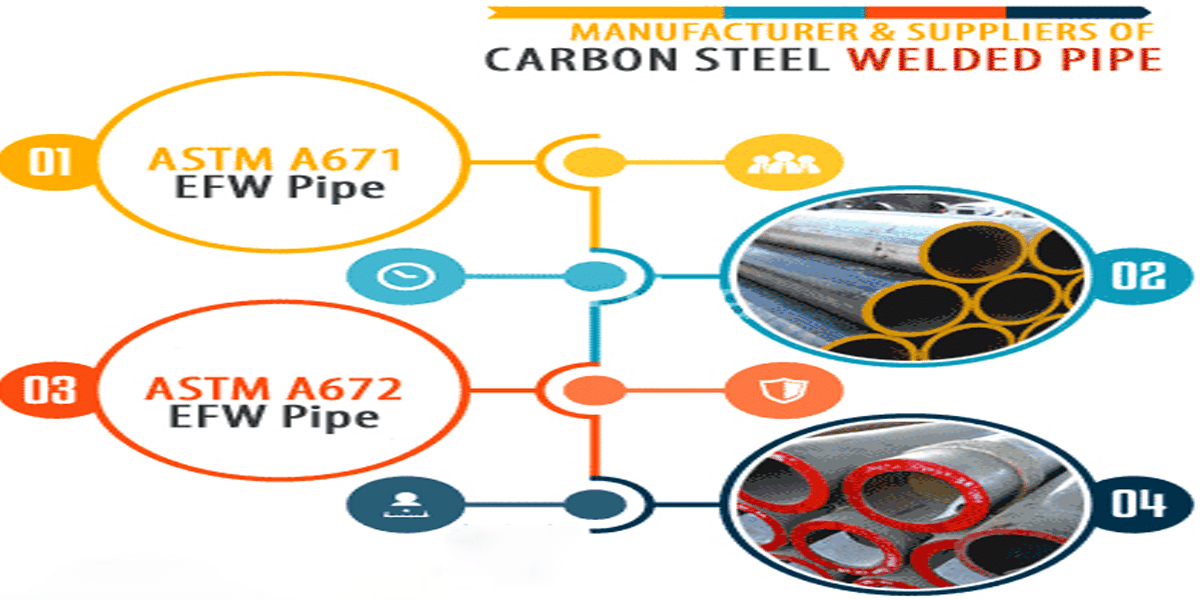
Manufacturing Process and Quality Control Differences between ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
1. Raw Material Selection
ASTM A671:
Utilizes steel plates (typically ASTM A516, A285, etc.) made of carbon or low-alloy steel. These plates are certified according to specific standards and are classified by grade (e.g., CC60, CC65, CC70) depending on the intended pressure and temperature service.
Focus: Strength and high-temperature resistance.
ASTM A672:
Also uses steel plates, often A515 or A537, but places greater emphasis on structural strength and wall thickness uniformity. This makes it suitable for large-diameter, thick-walled pipes.
Focus: Mechanical strength and structural integrity.
2. Welding Methods
ASTM A671: Primarily uses arc welding or submerged arc welding (SAW). In many cases, double-sided welding is performed to improve joint quality. Weld procedures must be qualified through Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) and procedure qualification tests.
ASTM A672: Uses similar welding techniques but often involves multi-pass welding due to thicker wall sections. Greater control of heat input is required to maintain weld integrity and reduce residual stress.
3. Heat Treatment and Post-Weld Processing
ASTM A671: Typically requires normalizing or normalizing plus tempering to improve microstructure uniformity and relieve residual stress. For certain grades and service conditions, post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) is mandatory to ensure long-term performance under high pressure and temperature.
ASTM A672: Heat treatment requirements are more flexible and depend on the application. For thick-walled structures, partial or full heat treatment may be applied to relieve stress and improve dimensional stability.
4. Inspection and Quality Control
ASTM A671:
Requires more rigorous inspection, including:
100% non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing
Mechanical testing (tensile, impact, hardness)
Chemical composition analysis
Weld coupon testing and metallographic inspection
Often aligned with ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code standards for use in pressure systems.
ASTM A672: Similar inspection methods are used, but the focus is typically on wall thickness uniformity, weld formation quality, and structural strength. Radiographic testing coverage may vary depending on the grade and project requirements.
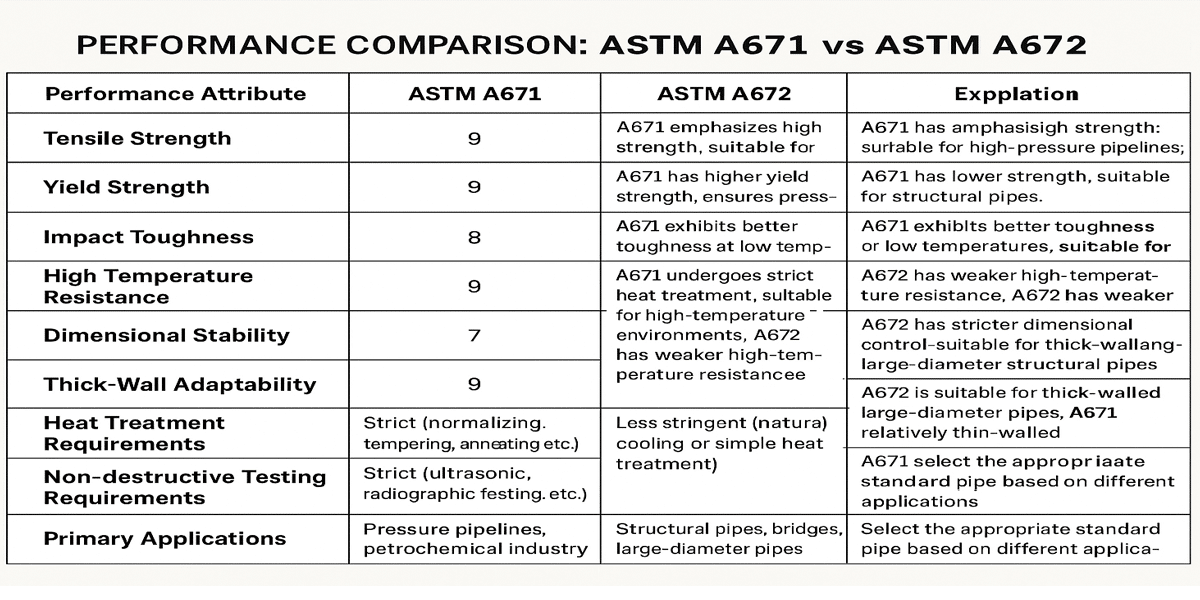
Performance Comparison of ASTM A671 vs ASTM A672
Application Scope
ASTM A671: Primarily used for high-pressure and high-temperature applications such as boilers, pressure vessels, and heat exchangers.
ASTM A672: Mainly used for structural purposes, including bridges, machinery, and building frameworks.
Mechanical Properties
ASTM A671: Offers a range of grades with specific tensile and yield strengths suitable for pressure containment and thermal stresses.
ASTM A672: Focuses on higher strength and toughness for structural load-bearing requirements.
Chemical Composition
ASTM A671: Contains controlled alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to improve corrosion and heat resistance.
ASTM A672: Chemical composition is optimized for weldability and mechanical strength rather than corrosion resistance.
Temperature and Pressure Resistance
ASTM A671: Designed to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures typical of pressure vessels and boilers.
ASTM A672: Suitable for ambient temperature structural applications with moderate pressure requirements.
Welding and Fabrication
ASTM A671: Requires precise welding techniques and stringent quality control due to its application in critical pressure systems.
ASTM A672: Welding requirements are focused on maintaining structural integrity with relatively more flexibility.
Inspection and Testing
ASTM A671: Subject to rigorous non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic and radiographic inspections to ensure safety.
ASTM A672: Testing mainly includes mechanical property verification and visual inspection, less intensive than A671.
Cost Considerations
ASTM A671: Generally more expensive due to alloy content and stringent quality standards.
ASTM A672: More cost-effective for structural uses without demanding high-temperature resistance.
Detailed introduction of ASTM A671 and ASTM A672
1. Overview and Application of ASTM A671
1. Standard Overview
ASTM A671 is a standard issued by ASTM International for Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) and Electric Fusion Welded (EFW) alloy and carbon steel pipes. It is mainly used for manufacturing pipes that withstand certain pressure and environmental conditions, commonly applied in petroleum, natural gas, mechanical structures, boilers, and shipbuilding.
2. Application Scenarios
Pressure piping for fluid transport: such as oil, natural gas, and chemical pipelines, especially where high strength and corrosion resistance are required.
Boilers and heat exchangers: suitable for manufacturing pressure-bearing boiler tubes and heat exchanger tubes, needing to resist high temperature and pressure.
Mechanical structural pipes: used in industrial machinery frameworks, bridges, and building structures requiring high strength and good weldability.
Automotive and agricultural machinery: for manufacturing frames, support structures, etc.
3. Key Performance Features
Covers various alloy and carbon steels with high strength and toughness.
Suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Excellent weldability and formability.
Different Grades and Classes available to meet specific needs.
2. Overview and Application of ASTM A672
1. Standard Overview
ASTM A672 focuses on welded structural steel pipes, emphasizing welding processes and post-weld heat treatment performance control. It is commonly used where structural strength and safety requirements are high.
2. Application Scenarios
Pressure vessels and pressure piping: suitable for pipelines that withstand high pressure, especially requiring heat treatment to improve performance.
Structural steel pipes for construction: bridges, steel structures, and municipal engineering where pipes require high strength and toughness.
Machinery manufacturing: mechanical structural components and equipment frames.
Oil and gas pipelines: especially in complex environments demanding excellent crack resistance.
3. Key Performance Features
Emphasizes weld quality and consistent post-heat-treatment performance.
Typically uses high-strength low-alloy steels.
Good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Suitable for pipes exposed to vibration and impact.
3. Selection Suggestions:
Choose ASTM A671 if the project requires high-temperature, high-pressure piping and mechanical structural pipes with a variety of material grades.
Choose ASTM A672 if the project demands high structural strength and toughness of welded pipes with post-weld heat treatment.
Consider the safety factor and operating environment (e.g., vibration, impact) to decide on heat treatment and material grade.
Ensure the selected pipe meets project mechanical properties and testing standards.
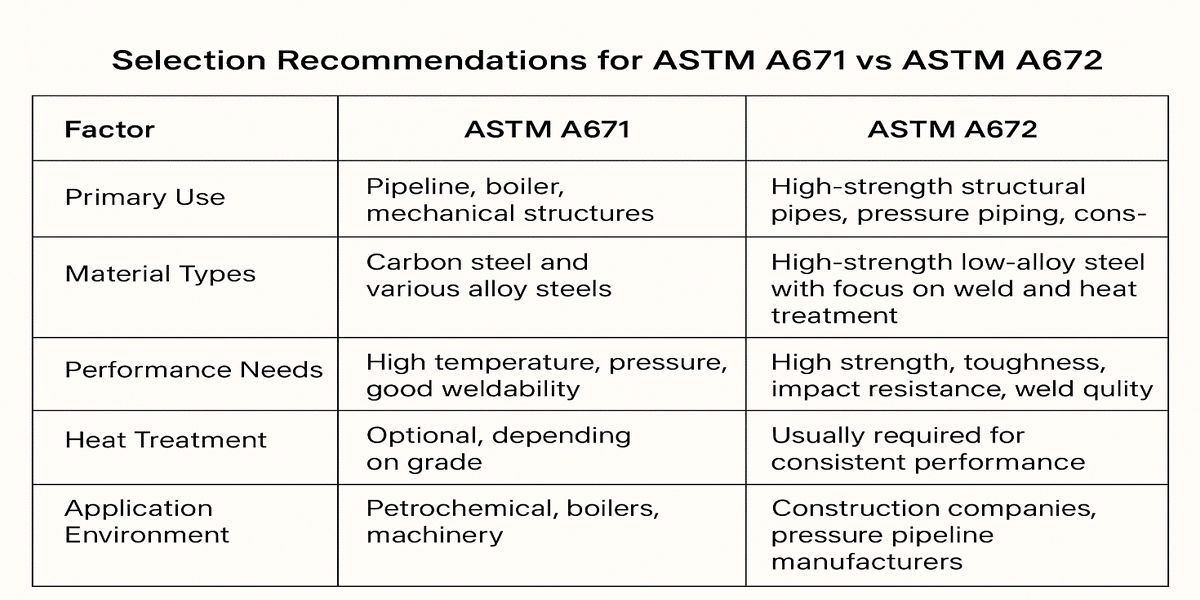
How to Correctly Choose ASTM A671 or ASTM A672 Steel Pipes in a Project?
1. Understand the Standards and Application Differences
ASTM A671:
Mainly applies to the manufacturing of low-alloy and carbon steel welded and seamless pipes used in boilers, pressure vessels, and heat exchangers under high temperature and high pressure conditions.
Suitable for pressure piping and vessel applications, emphasizing high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
ASTM A672:
Mainly used for structural welded steel pipes, focusing on structural strength and mechanical properties, suitable for machinery structures, bridges, building frameworks, and other load-bearing applications.
Ideal for applications requiring high strength and toughness.
2. Choose Based on Specific Project Requirements
ASTM A671: Pressure Vessel/Piping, High temperature performance, pressure resistance, corrosion resistance
ASTM A672: Structural Load-Bearing, Mechanical properties (strength, toughness, impact resistance), weldability
3. Select Based on Mechanical and Chemical Properties
Mechanical Properties:
ASTM A671 pipes have various grades (e.g., Grade 30, 40, 50) for different pressure and temperature conditions.
ASTM A672 pipes focus on tensile and yield strength to meet structural load demands.
Chemical Composition:
ASTM A671 pipes have stricter control over alloying elements (like Ni, Cr, Mo) to ensure high temperature and corrosion resistance.
ASTM A672 pipes focus more on weldability and structural strength.
4. Consider Project Operating Conditions
Operating Temperature and Pressure
For high temperature and high pressure, ASTM A671 is recommended.
For normal temperature structural use, ASTM A672 is preferable.
Environmental Conditions
For corrosion resistance or oxidation resistance in pressure piping, A671 is better.
For building structures or mechanical frameworks, A672 meets strength and safety needs.
5. Production Process and Inspection Requirements
Welding Process: Both are welded pipes but have different welding process standards due to their distinct applications. Strict adherence to the respective welding codes is required.
Inspection Standards:
ASTM A671 pipes generally require pressure testing and non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing to ensure safety.
ASTM A672 pipes focus on mechanical property tests, dimensional and visual inspection.
6. Cost and Procurement Recommendations
Cost Difference: A671 pipes are usually more expensive due to alloy content and performance requirements.
Project Budget: Choose based on budget to avoid over-design and waste.
Supplier Qualification: Select qualified and experienced suppliers to ensure compliance with ASTM standards and project needs.
In summary, both ASTM A671 and ASTM A672 steel pipes serve distinct purposes and are designed to meet different performance requirements. ASTM A671 is ideal for high-temperature, high-pressure applications such as boilers and pressure vessels, offering superior corrosion resistance and heat tolerance. On the other hand, ASTM A672 excels in structural applications where strength, toughness, and weldability are paramount.
Choosing the right standard depends on a thorough understanding of your project’s specific operating conditions, mechanical demands, and environmental factors. Careful consideration of these factors will not only ensure safety and performance but also optimize cost-effectiveness and longevity of the piping system. By aligning your material selection with these guidelines, you can confidently select the appropriate steel pipe standard to meet your project’s unique needs and ensure long-term success!