- 1. The Importance of Life Cycle Cost (LCC) in Steel Pipe Selection
- 2. Life Cycle Analysis of FBE Coated Steel Pipe
- 3. Life Cycle Analysis of 3PE Coated Steel Pipe
- 4. Cost-Effectiveness Comparison of FBE and 3PE Coated Steel Pipes
- 5. Typical Project Case Analysis
- 6. Making a steel pipe selection decision based on Lifecycle Cost (LCC)
In modern infrastructure development, material selection goes beyond initial investment—it directly impacts the lifecycle cost of a project. Especially in long-term systems like water or oil transportation, achieving optimal cost-effectiveness while ensuring durability is a major concern. Compared to conventional pipes, coated steel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance, significantly reducing future maintenance costs.
This article explores TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) steel pipe cost evaluation, compares popular coatings such as FBE vs 3PE, and discusses strategies for selecting the right corrosion-resistant coated steel pipe. The goal is to provide practical insights and recommendations for infrastructure pipe applications that balance performance and long-term savings!
The Importance of Life Cycle Cost (LCC) in Steel Pipe Selection
Life Cycle Cost (LCC) refers to the total cost incurred throughout a product’s entire lifespan—from procurement and installation to operation, maintenance, and eventual disposal. In infrastructure projects, focusing solely on initial costs often leads to higher long-term expenditures due to frequent repairs or replacements. LCC provides a comprehensive perspective for evaluating true cost-effectiveness in material selection.
Key factors affecting LCC include: initial purchase and installation costs, ongoing maintenance costs, expected service life, repair frequency, and potential downtime losses.
In the case of coated steel pipes, their typical service life in infrastructure applications ranges from 30 to 50 years—significantly longer than bare steel pipes—thanks to their superior corrosion resistance. For example, FBE vs 3PE coatings perform differently under varying conditions: FBE is well-suited for moderate environments with lower upfront costs, while 3PE is ideal for harsh, corrosive settings, offering enhanced durability and longer life, making it a preferred option in TCO steel pipe cost evaluations.
To optimize long-term performance and savings, pipe selection should align with environmental factors, fluid types, and project lifespan goals. A well-informed coated steel pipe selection strategy enables better infrastructure pipe recommendations and ensures full lifecycle cost control.
Life Cycle Analysis of FBE Coated Steel Pipe
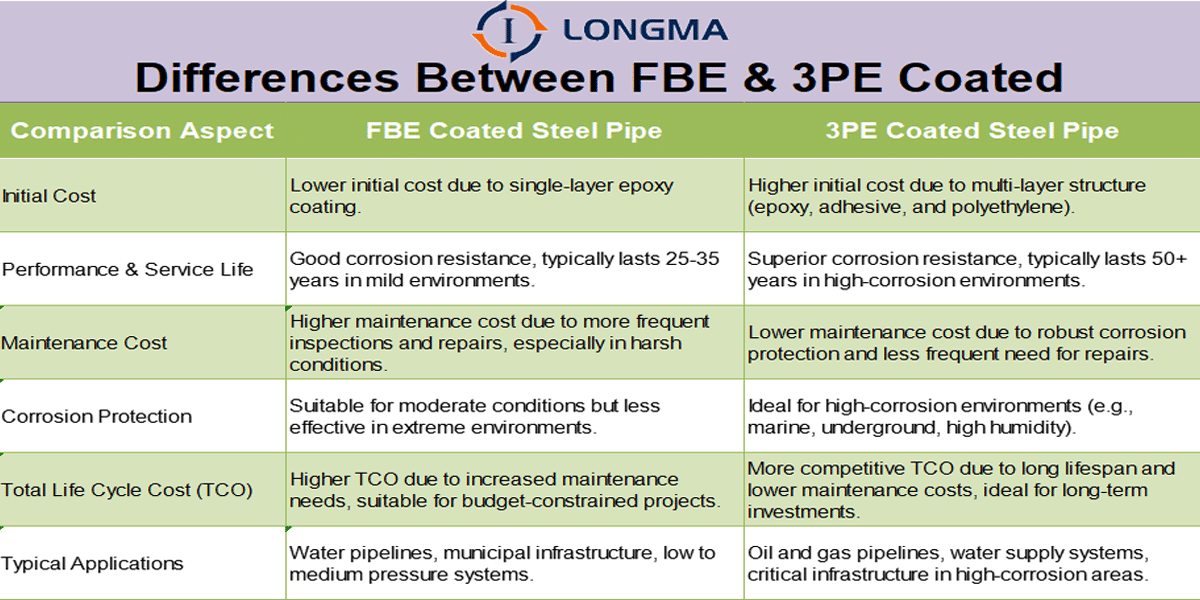
1. Cost: FBE (Fusion Bonded Epoxy) coated steel pipes have a relatively low initial procurement cost, significantly lower than multi-layer coatings like 3PE. For infrastructure projects with budget constraints, FBE is a cost-effective option. In TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) steel pipe cost evaluations, FBE offers excellent cost-effectiveness in moderate environments, balancing initial investment with long-term performance.
2. Performance & Service Life: Under proper installation and suitable conditions, FBE coated steel pipes typically have a service life of 25 to 35 years. The strong adhesion between the epoxy coating and the steel pipe effectively protects against soil corrosion, moisture, and mild chemical exposure, making them ideal for water transmission, municipal pipelines, and low to medium-pressure oil and gas systems. These pipes are commonly recommended for infrastructure applications.
3. Maintenance: In dry or neutral environments, FBE coated pipes generally require minimal maintenance. However, in high-moisture or aggressive environments, the coating may experience wear, peeling, or aging, leading to higher maintenance needs. Compared to 3PE coatings, FBE may have slightly higher maintenance costs but remains advantageous in moderate conditions due to its overall lifecycle cost.
Life Cycle Analysis of 3PE Coated Steel Pipe
1. Cost: Compared to FBE-coated steel pipes, 3PE coated steel pipes have a higher initial procurement cost. Their multi-layer structure, consisting of an epoxy powder layer, a bonding layer, and a polyethylene protective layer, provides superior corrosion protection, which leads to a higher upfront investment. However, considering their excellent corrosion resistance and longer service life, TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) analysis shows that 3PE pipes are more cost-effective in the long term, especially in harsh environments.
2. Performance & Service Life: 3PE coated steel pipes perform exceptionally well in high-corrosion environments, making them suitable for extreme conditions like marine environments, underground applications, and high humidity areas. Their service life typically exceeds 50 years, significantly longer than FBE-coated pipes. With superior corrosion resistance, 3PE-coated pipes are ideal for oil and gas pipelines, water supply systems, and other critical infrastructure that require long-term durability and reliability.
3. Maintenance: Despite their long service life and robust corrosion protection, 3PE-coated pipes may still experience coating damage or wear in extreme conditions, potentially leading to localized leaks or corrosion. Regular inspections and necessary coating repairs are still essential. However, compared to FBE-coated pipes, maintenance costs for 3PE pipes are lower due to their strong durability and reduced need for frequent repairs, especially in corrosive environments.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison of FBE and 3PE Coated Steel Pipes
1. Initial Cost
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: FBE (Fusion Bonded Epoxy) coatings have a lower initial investment as the single-layer epoxy coating is less expensive compared to 3PE. This makes FBE a more attractive option for projects with limited budgets.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: Due to the three-layer structure (epoxy powder layer, adhesive layer, and polyethylene protective layer), 3PE coated pipes have a higher initial cost. The multi-layer coating offers superior corrosion protection but increases the upfront investment.
2. Performance & Service Life
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: FBE coatings provide good corrosion resistance, but they are more suitable for milder environments (e.g., standard water transmission pipelines). The service life typically ranges from 25 to 35 years.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: 3PE coatings offer excellent corrosion protection, making them ideal for highly corrosive environments (e.g., marine, underground, or high-humidity areas). Their service life can exceed 50 years, making them a better choice for harsh conditions.
3. Maintenance Cost
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: While FBE coatings have lower initial costs, they are more prone to damage in corrosive environments and may require more frequent inspections and repairs, resulting in higher long-term maintenance costs.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: Due to the superior corrosion resistance of the three-layer structure, 3PE-coated pipes have a lower frequency of required maintenance. They generally incur lower maintenance costs over time, especially in corrosive environments.
4. Total Life Cycle Cost (TCO)
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: Although FBE-coated pipes have lower initial costs, the need for more frequent maintenance in high-corrosion environments leads to higher TCO in the long run. They are suitable for projects with budget constraints or for use in milder environments.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: Although the initial investment is higher, the superior corrosion resistance and lower maintenance costs of 3PE-coated pipes result in a more competitive TCO. They are ideal for long-term investments, especially in corrosive environments.
Typical Project Case Analysis
1. FBE Coated Steel Pipe Application Case
Project Name: Municipal Water Supply Pipeline Project
Location: Urban area, low to medium corrosion environment
Project Background: This project involves the construction of the city’s water pipeline network. The water source is stable, and the soil corrosion is mild, making it suitable for FBE coated steel pipes.
Coating Type Used: Single-layer Fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE)
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis:
Lower initial cost, ideal for projects with limited budgets.
Performance of FBE coating is sufficient for urban environments with mild corrosion, ensuring the proper operation of the pipeline system.
Low maintenance required, making it suitable for low to medium corrosion environments.
2. 3PE Coated Steel Pipe Application Case
Project Name: Offshore Oil & Gas Pipeline Project
Location: Marine environment, high corrosion exposure
Project Background: This project involves the construction of an offshore oil and gas pipeline, which is subject to severe corrosion from seawater, salt, and humidity.
Coating Type Used: Three-layer Polyethylene (3PE) Coating (epoxy powder layer, adhesive layer, and polyethylene protective layer)
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis:
Higher initial cost, but the multi-layer structure of 3PE provides superior corrosion protection, ensuring long-term durability in extreme environments.
Long service life, typically over 50 years, significantly reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement.
Despite the higher upfront investment, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is lower in the long run, considering reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
Making a steel pipe selection decision based on Lifecycle Cost (LCC)
Making a steel pipe selection decision based on Lifecycle Cost (LCC) is essential for ensuring the most cost-effective choice, considering long-term operation and maintenance. Here’s how to approach steel pipe selection using lifecycle cost analysis:
1. Define Project Requirements and Environmental Conditions
Start by understanding the project’s basic needs and the environmental conditions (e.g., corrosion level, pressure requirements). Environmental factors directly influence the performance of steel pipes and dictate the coating and material requirements.
Corrosive Environment: If the steel pipe is exposed to a highly corrosive environment (e.g., marine, underground, or high-humidity areas), consider more protective coating options such as 3PE coated steel pipes.
Pressure and Fluid Type: The type of fluid (e.g., oil, gas, water, chemicals) and its pressure rating will affect the material and coating choice.
2. Estimate Initial Investment Costs
Initial investment is the most direct cost consideration in pipe selection. Different types of coated steel pipes, such as FBE coated steel pipes and 3PE coated steel pipes, come with varying material and coating costs.
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: Lower initial cost, ideal for projects with limited budgets and environments with minimal corrosion.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: Higher initial cost, but provide superior protection in highly corrosive environments, making them suitable for more demanding projects.
3. Evaluate Long-Term Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs are a crucial part of lifecycle costs. Steel pipes, over time, may require regular inspection, repair, or replacement due to corrosion and wear. Choosing a pipe with long-lasting protective coatings can significantly reduce future maintenance costs.
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: While initial costs are lower, more frequent inspections and repairs may be necessary, especially in corrosive environments, increasing long-term maintenance costs.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: With superior corrosion protection, these pipes typically require less frequent maintenance, reducing the need for repairs and lowering overall maintenance costs.
4. Consider Pipe Service Life
The service life of a steel pipe is a key factor in determining its total lifecycle cost. A pipe with a longer service life may have a higher initial cost, but it often results in lower total costs over time.
FBE Coated Steel Pipes: Suitable for less corrosive environments, with a service life typically ranging from 25 to 35 years. However, this lifespan can vary based on the specific conditions of the project.
3PE Coated Steel Pipes: Typically offer a service life of 50+ years, especially in harsh environments. Although initial costs are higher, the long service life contributes to lower overall lifecycle costs.
5. Total Lifecycle Cost (TCO) Analysis
TCO is the comprehensive analysis of all costs associated with the steel pipe throughout its entire lifecycle, including:
Initial Investment: The cost of pipe procurement and installation.
Operational Costs: Regular inspection, monitoring, and operational costs.
Maintenance and Repair Costs: Expenses incurred from maintaining and repairing pipes due to corrosion, damage, etc.
Replacement Costs: The cost of replacing the pipe at the end of its service life.
By comparing the TCO of different coatings, you can choose the pipe type that offers the lowest overall lifecycle cost while meeting performance and environmental requirements.
6. Select the Appropriate Coating and Pipe Type
Based on the assessments above, consider:
Initial Budget.
Long-Term Maintenance Needs.
Service Life of the Pipe.
Make a decision that balances initial cost and long-term economic efficiency. For example, FBE coated steel pipes may be ideal in environments with mild corrosion and limited budgets, while 3PE coated steel pipes provide superior long-term cost-effectiveness in corrosive environments despite their higher upfront costs.
In modern infrastructure planning, selecting the right coated steel pipe requires a forward-looking approach that goes beyond initial costs. By applying lifecycle cost analysis (LCC), engineers and decision-makers can holistically evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), balancing initial investment, maintenance costs, and long-term performance and service life. Whether choosing FBE or 3PE coated steel pipes, understanding their respective strengths and lifecycle profiles helps ensure cost-effective, durable, and low-maintenance solutions for critical infrastructure. In the end, a smart selection driven by LCC not only enhances project sustainability, but also delivers lasting value across the entire pipe system lifecycle!