- 1. EN 10219 Standard: Detailed Explanation of Definition and Scope of Application
- 2. Manufacturing Characteristics of Cold-Formed Structural Hollow Sections – Detailed Explanation
- 3. Interpretation of the Structure and Implementation of EN 10219
- 4. Common Steel Grades and Performance Comparison under EN 10219
- 5. Comparison of EN 10219 with Other Steel Tube Standards
- 6. Application Scenarios and Case Studies of EN 10219 Steel Tubes
- 7. Key Considerations When Purchasing EN 10219 Steel Tubes
As modern construction and engineering projects increasingly pursue efficiency and lightweight design, cold-formed steel tubes are becoming a key choice in structural design. Recognized as one of the leading European standards, EN 10219 is being widely adopted across various projects, especially for its advantages in high strength, sustainability, and precision manufacturing. This article offers a quick Introduction to the EN 10219 Standard, while also addressing common topics such as EN 10219 Rectangular and Square Tube Specifications Explained, Differences Between S355J2H and S235JRH, and more—helping you make informed decisions when selecting structural hollow sections. If you’re looking for a practical Cold-Formed Structural Steel Standard Selection Guide, you won’t want to miss this.
EN 10219 Standard: Detailed Explanation of Definition and Scope of Application
I. Standard Definition
EN 10219 is an authoritative technical standard established by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). Its full title is “Cold formed welded structural hollow sections of non-alloy and fine grain steels – Technical delivery conditions.”
This standard specifically applies to welded structural hollow sections manufactured through cold-forming processes. It defines comprehensive technical requirements covering the entire production chain—from raw materials to finished products—serving as a critical reference in the field of steel structure engineering.
II. Scope of Application
1. Product Types
Covers welded closed-section steel products formed by cold rolling, including:
Square Hollow Sections (SHS)
Rectangular Hollow Sections (RHS)
Circular Hollow Sections (CHS)
For detailed dimensional specifications, refer to “EN 10219 Square and Rectangular Hollow Section Specifications.”
2. Material Grades
Applies to non-alloy and fine-grain steels, with common grades such as: S235J0H, S235J2H
Other specialized steel grades for specific applications
3. Application Fields
Building structures: High-rise buildings, long-span spatial structures
Infrastructure: Bridges, platforms, transmission towers
Mechanical engineering: Crane booms, equipment frameworks
Compliant with “Guide to Selecting Cold-Formed Structural Steel Standards” for sustainable construction projects
Manufacturing Characteristics of Cold-Formed Structural Hollow Sections – Detailed Explanation
Cold-formed structural hollow sections are widely used in construction, bridges, and machinery due to their lightweight nature, high strength, and ease of fabrication. Their manufacturing process differs significantly from hot-rolled sections, with the following key characteristics:
1. Cold Forming Process
Definition: Shaping steel strips or plates at room temperature through rolling, bending, and welding rather than hot rolling.
Features:
High precision: Strict dimensional tolerances (e.g., ±1% side length tolerance per EN 10219) with smooth surfaces.
Material efficiency: Reduced waste compared to hot rolling, suitable for customized production.
Work hardening: Cold deformation increases strength but may reduce ductility, requiring controlled forming speeds.
2. Welding Technology
High-Frequency Welding (HFW):
Uses high-frequency current to heat and pressure-weld steel edges, ensuring stable, high-quality seams.
Ideal for mass production of standard square/rectangular tubes (see EN 10219 Square and Rectangular Hollow Section Specifications).
Arc Welding (SAW/ERW):
Used for thick-walled or special-shaped tubes, offering higher weld strength at greater cost.
3. Material Properties
Common steel grades:
Non-alloy steels (e.g., S235JRH) and fine-grained steels (e.g., S355J2H), compliant with EN 10219 chemical/mechanical requirements.
Grade selection impacts cost/performance (refer to Differences Between S355J2H and S235JRH).
Formability:
Ultrasonic testing (UT) to inspect weld integrity.
Hydrostatic or eddy current testing for leak-proof verification.
Requires high ductility to prevent cracking or springback during cold forming.
4. Dimensional Control
Cross-sections: Square (SHS), rectangular (RHS), circular (CHS), and custom profiles.
Wall uniformity: More consistent than hot-rolled products, ideal for precision structures.
Straightness: Must meet standard limits (e.g., ≤1.5mm/m per EN 10219).
5. Post-Processing & Testing
Heat treatment: Annealing may be required for high-strength steels to relieve residual stresses.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Surface treatment: Galvanizing or painting for corrosion resistance.
6. Advantages vs. Limitations
Advantages:
Lightweight design reduces structural loads.
Flexible shaping for complex architectures (e.g., curved structures).
Limitations:
Stress concentration risks require design considerations.
Production challenges for large/thick-walled sections may necessitate hot-rolled alternatives.
Interpretation of the Structure and Implementation of EN 10219
EN 10219 is the European standard specifically developed for cold-formed welded structural hollow sections. It covers critical aspects such as material selection, manufacturing requirements, testing procedures, dimensional tolerances, and delivery conditions. The standard is well-structured and systematically implemented, offering a clear framework for manufacturers, designers, and contractors.
1. Overview of the Standard Structure
EN 10219 is divided into two main parts:
EN 10219-1: Technical Delivery Conditions
This part specifies:
Applicable steel grades (e.g., S235JRH, S275J2H, S355J2H — non-alloy and fine grain structural steels)
Requirements for chemical composition and mechanical properties
Technical conditions for cold forming and welding
Inspection, testing, and acceptance standards (e.g., tensile tests, impact tests, non-destructive testing)
Marking and certification requirements (e.g., EN 10204 compliance)
EN 10219-2: Tolerances, Dimensions and Sectional Properties
This section includes:
Standard dimensions for square, rectangular, and circular hollow sections
Permissible tolerances for wall thickness, corner radius, straightness, ovality, etc.
Sectional properties tables — such as cross-sectional area, moment of inertia, and section modulus — used for structural design
Together, these parts form a comprehensive technical and quality framework from raw material to final product.
2. Implementation Methodology
The execution of EN 10219 involves several key processes:
a. Material Selection
Manufacturers must select steel grades that comply with the standard and perform necessary tests to verify each batch. Common grades such as S235JRH and S355J2H are selected based on specific strength and toughness requirements.
Related: Differences between S355J2H and S235JRH
b. Controlled Production
Cold forming, welding, and shaping must be carried out under controlled conditions to ensure dimensional accuracy and weld quality. All tolerances — such as for diagonals, wall thickness, and twist — must fall within EN 10219-2 limits.
c. Testing & Inspection
Mandatory tests include:
Tensile test
Charpy V-notch impact test
Chemical composition analysis
Non-destructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic or eddy current inspection for weld seams)
All results must be documented and reflected in the material test certificate (e.g., EN 10204 Type 3.1).
d. Product Marking & Certification
Qualified EN 10219 products must be clearly marked with:
Section type and dimensions
Steel grade (e.g., S355J2H)
Standard reference (EN 10219)
Batch number and manufacturer information
This ensures full traceability throughout design and construction phases.
e. Design Integration
EN 10219 products are fully compatible with Eurocode 3, allowing structural engineers to use sectional property data directly for precise calculations.
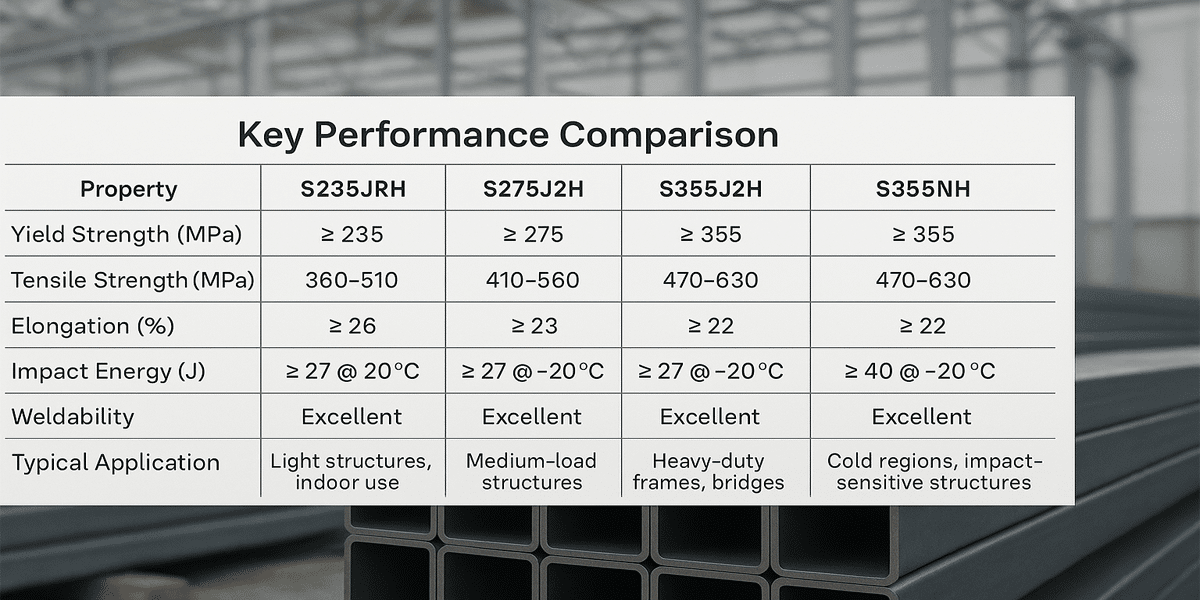
Common Steel Grades and Performance Comparison under EN 10219
1. Overview of Standard Steel Grade System
Naming Convention
Alphanumeric structure (e.g., S355J2H):
S: Structural steel
355: Minimum yield strength (MPa)
J2: Charpy impact energy guarantee (27J @ -20°C)
H: Designation for hollow sections
Main Steel Grade Categories
Standard strength: S235J0H/J2H, S275J0H/J2H
High strength: S355J0H/J2H, S420MH
Special applications: S460NH (seismic), S550Q (ultra-high strength)
2. Common Steel Grades
S235JRH
A non-alloy structural steel with relatively low yield strength and good cost efficiency. It is suitable for light structures and non-load-bearing components, widely used in economical projects.
S275J2H
Also a non-alloy structural steel, with higher yield strength than S235JRH. It offers good weldability and impact toughness, suitable for medium-strength structural applications.
S355J2H
A fine grain structural steel with high yield strength, combining good plasticity and toughness. It is the most widely used high-strength steel grade in building and industrial structures, ideal for load-bearing members.
S355NH
Similar in performance to S355J2H but better suited for low-temperature environments, offering enhanced impact toughness. Commonly used in cold regions or where high toughness is required.
Note: “H” stands for hollow section. “J2” indicates impact toughness tested at -20°C. “N” refers to normalized or equivalent heat treatment.
3. Steel Grade Selection Advice
Depending on the structural requirements and environmental conditions, here are some practical suggestions:
For lightweight indoor structures or non-load-bearing applications, S235JRH offers an economical choice.
For general construction requiring moderate strength, S275J2H is a balanced option, while S355J2H is the most widely used high-strength grade for industrial and structural engineering.
For projects in cold climates or needing enhanced toughness, S355NH is recommended due to its reliable low-temperature performance.
When reviewing EN 10219 square and rectangular tube specifications, selecting the right steel grade based on the load-bearing needs is essential.
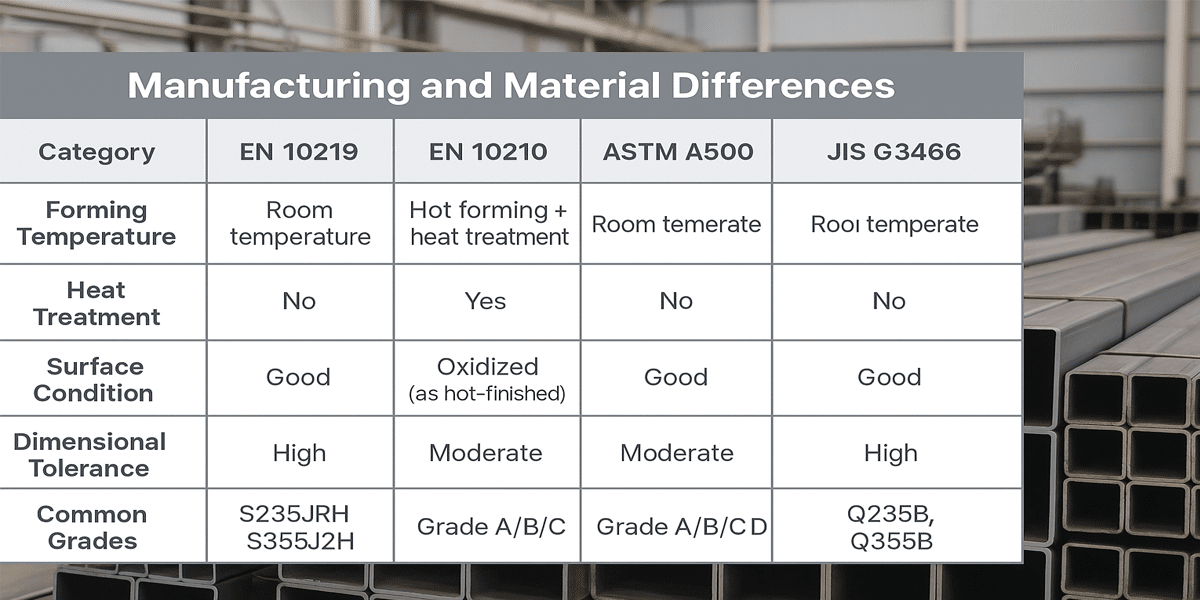
Comparison of EN 10219 with Other Steel Tube Standards
EN 10219 is the European standard for cold-formed welded structural hollow sections (such as square, rectangular, and circular tubes). It is widely used in structural engineering, steel construction, and industrial frameworks. Compared with other regional or international standards—such as EN 10210, ASTM A500, JIS G3466, and GB/T 6728—it differs in manufacturing methods, mechanical properties, and testing requirements.
1. Difference between them:
EN 10219 emphasizes precision in cold-forming and weld quality, ideal for modern modular construction.
Compared to EN 10210, EN 10219 is more cost-effective but offers slightly lower impact resistance.
Compared to ASTM A500, EN 10219 applies stricter requirements in testing and impact performance.
2. Overview of Major Standards
EN 10219
Cold-formed welded hollow sections, widely used in European construction and structural frames.
EN 10210
Hot-finished hollow sections with heat treatment, suitable for heavy-duty and seismic-resistant structures.
ASTM A500
US standard for cold-formed welded steel tubes, common in buildings, machinery, and supports.
JIS G3466
Japanese standard for cold-formed rectangular tubes, used in light structures and equipment frames.
GB/T 6728
Chinese standard for cold-formed square and rectangular tubes, popular in general construction and transportation.
3. Manufacturing and Material Differences
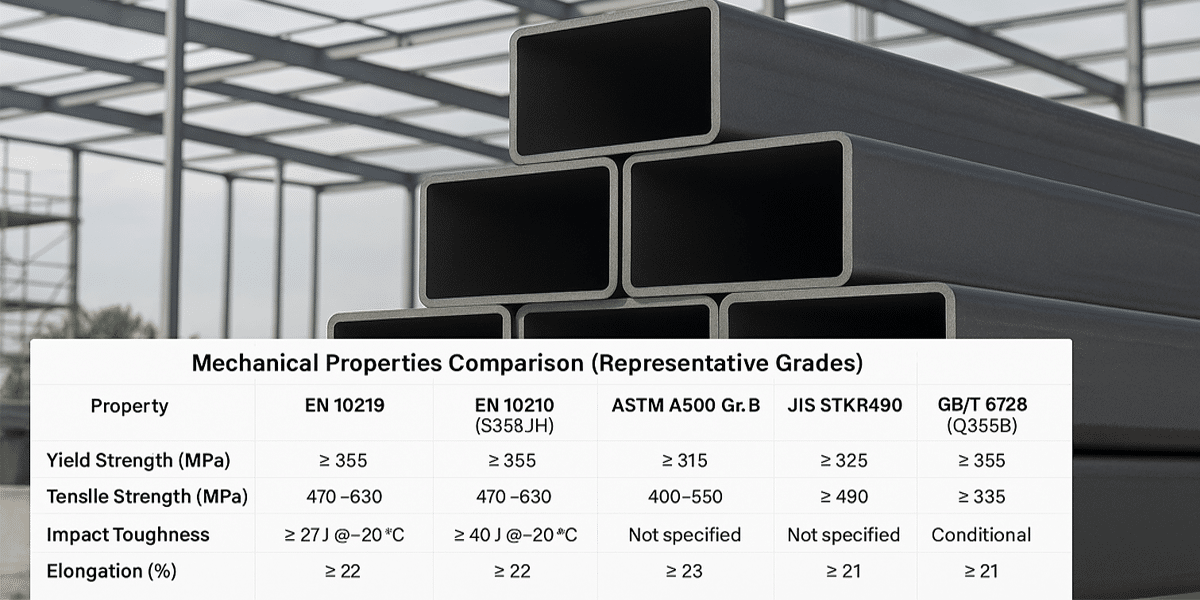
4. Mechanical Properties Comparison (Representative Grades)
Application Scenarios and Case Studies of EN 10219 Steel Tubes
EN 10219 cold-formed welded hollow sections (including square, rectangular, and circular tubes) are widely used across various industries thanks to their high strength, light weight, excellent dimensional accuracy, and good weldability. Their applications span not only structural construction but also mechanical, transportation, and energy sectors.
1. Building and Structural Engineering
Key Features: Lightweight, high strength, easy to assemble, compatible with Eurocode structural design.
Typical Cases:
Curtain Wall Frames for High-rise Buildings: EN 10219 S355J2H rectangular tubes are used for load-bearing frames that also serve aesthetic functions.
Airport Terminal Roof Structures: Large-size rectangular sections form spatial trusses with high seismic resistance and stiffness.
Industrial Warehouses & Logistic Centers: Used in column-beam systems with high dimensional precision, supporting modular and fast construction.
2. Bridges and Municipal Infrastructure
Key Features: Customizable lengths and cross-sections, excellent durability in outdoor environments.
Typical Cases:
Pedestrian Bridge Railings and Trusses: Lightweight rectangular hollow sections offer modern appearance and structural reliability.
Urban Landscape Bridges: Cold-formed steel tubes are used to create curved beams that integrate lighting and railing systems for visual appeal.
3. Industrial Machinery and Equipment Frames
Key Features: Compact structures, strong load-bearing capacity, easy to weld and fabricate.
Typical Cases:
Automation Equipment Support Frames: Medium and small-size EN 10219 S275J2H tubes provide solid, weldable support.
Solar Tracking Systems: Long-span S355J2H high-strength sections effectively resist wind and dynamic loads.
Crane Base Frames and Substructures: Hollow steel sections reduce self-weight while maintaining sufficient stiffness.
4. Transportation and Energy Infrastructure
Key Features: Long service life, fatigue resistance, ideal for dynamic or harsh conditions.
Typical Cases:
Highway Sign Poles and Lighting Masts: Circular or octagonal sections manufactured per EN 10219, with high wind and corrosion resistance.
Wind Turbine Internal Support Frames: Hollow sections used for platform beams and lateral bracing ensure structural safety.
Subway and Rail Station Guardrails: Small-size cold-formed hollow sections create safe, durable, and aesthetically pleasing barriers.
5. Architectural Aesthetics and Prefabricated Systems
Key Features: Versatile profiles, suitable for modular design, modern and clean appearance.
Typical Cases:
Prefabricated Building Columns and Beams: Rectangular tubes easily integrate with precast panels, improving on-site efficiency.
Architectural Installations and Public Facilities: Used in sculptures, pavilions, and lightweight canopies to create artistic yet strong forms.
Stair Railings and Balustrades: Clean, polished EN 10219 square tubes serve both functional and decorative purposes.
Key Considerations When Purchasing EN 10219 Steel Tubes
Purchasing EN 10219 steel tubes involves evaluating several critical aspects such as product performance, compliance with standards, and supply chain reliability. To ensure you obtain high-quality cold-formed structural hollow sections that meet project requirements, consider the following factors:
1. Define Technical Requirements Clearly
Before purchasing, confirm the following parameters:
Steel Grade: Options like S235JRH, S275J2H, S355J2H offer varying yield strength and impact toughness.
Dimensional Specifications: Outer size, wall thickness, and tolerances must align with design drawings.
Section Shape: Choose square, rectangular, circular, or custom sections based on structural needs.
Impact Toughness Requirements: Some projects (e.g., seismic or low-temperature applications) require certified impact performance at -20°C or lower.
2. Verify Compliance with the EN 10219 Standard
Standard Edition: Ensure the supplier follows the latest EN 10219-1 and EN 10219-2.
Certification:
Request a valid EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 inspection certificate.
Check if the mill test reports include chemical composition, mechanical properties (yield, tensile, impact), dimensional tolerances, etc.
Factory Qualifications: Prefer manufacturers certified to ISO 9001, CE marking, or EN 1090 for structural steel.
3. Choose Experienced Manufacturers or Suppliers
Expertise in Cold-Formed Structural Steel: Look for those familiar with European or international project requirements.
Traceability: Can the supplier provide heat number tracking, barcoding, and full batch traceability?
Customization Capability: Can they provide cutting-to-length, drilling, hot-dip galvanizing, or coating services?
Delivery Reliability: Can they ensure timely and consistent delivery, especially for large-volume orders?
4. Pay Attention to Logistics and Packaging
Transportation: Ensure appropriate modes such as container shipping, flatbed trucks, or bulk vessels.
Corrosion Protection: Apply anti-rust oil, plastic wrapping, or plastic end caps for long-haul transport.
Labeling: Each tube should be labeled with grade, size, heat number, and order reference for identification.
EN 10219 steel tubes are becoming a top choice in modern construction for their strength, precision, and global standard compliance. Whether you’re designing, sourcing, or building—knowing this standard gives you a real edge. If this post helped you, tap like, save, and follow for more on EN 10219 tube specs, steel grade tips, and standard selection guides. Got questions? Let’s chat in the comments!




