In steel structures, equipment manufacturing, and construction projects, are you also struggling to decide which steel pipe to choose? Especially when it comes to EN 10219 vs EN 10210, they may look similar, but their uses differ greatly. One is a cold-formed steel pipe, the other is a hot-formed steel pipe—similar appearance, but with different performance, costs, and application scenarios. How can you quickly tell them apart? How to strike the right balance between structural safety, processing efficiency, and budget? That’s exactly what this article aims to help you with. Keep reading to get a clear understanding of the key differences between EN 10219 and EN 10210, and practical recommendations for steel pipe selection and comparison!

Definitions and Scope of EN 10219 and EN 10210
EN 10219 — Cold-formed Welded Structural Hollow Sections
EN 10219 primarily covers welded hollow steel sections manufactured by cold-forming processes. These steel pipes are formed by cold bending steel plates into shape and then welding them, resulting in high dimensional accuracy, smooth surfaces, and uniform cross-sections.
Typical applications include:
Structural supports
Frame structures
Building and bridge construction
Machinery frames
Light load-bearing structures
Due to strain hardening during the cold-forming process, EN 10219 pipes generally exhibit higher yield strength and good mechanical properties, with uniform wall thickness that facilitates precise machining and assembly.
EN 10210 — Hot-finished Structural Hollow Sections
EN 10210 applies to hot-formed solid or hollow steel sections. The manufacturing involves heating steel billets at high temperatures, followed by extrusion, rolling, or hot expansion forming. This process improves plasticity and toughness while minimizing defects, making these pipes suitable for heavy loads and complex stress conditions.
Typical applications include:
Heavy load-bearing structures
High-strength steel structures
Industrial machinery supports
Large-scale structures such as bridges and towers
Situations requiring higher impact toughness and corrosion resistance
Hot-formed steel tubes feature uniform wall thickness and stable cross-sectional dimensions, ideal for projects with stringent structural safety requirements.
Manufacturing Process Comparison: Cold-formed vs Hot-formed
1. Cold-formed Steel Pipes
Cold-formed steel pipes are produced by shaping steel plates at or near room temperature, followed by welding to form the pipe. The typical process includes:
Raw Material Preparation: Steel coils or sheets are flattened and cut for forming.
Forming Process: Steel plates are gradually bent into round or square shapes using cold bending rollers.
Welding: The edges are welded using high-frequency welding (HFW) or other welding methods to close the pipe.
Cooling and Shaping: After welding, the pipe cools naturally and undergoes dimensional correction and surface treatment.
Inspection and Cutting: The pipes are inspected for dimensions and quality, then cut to specified lengths.
Features and Advantages:
High production efficiency with relatively low equipment investment.
High dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish, facilitating subsequent machining and assembly.
The material experiences strain hardening, resulting in higher yield strength.
Suitable for light to medium load structures with relatively thin walls, saving material.
Limitations:
Cold forming introduces residual stresses and may reduce plasticity in some materials.
Difficulties and higher costs arise for thicker walls or larger sections.
Generally lower impact toughness and ductility compared to hot-formed pipes.
2. Hot-formed Steel Pipes
Hot-formed steel pipes are made by heating steel billets to high temperatures (usually above 900°C), where the steel becomes plastic and is then formed by extrusion, rolling, or hot expansion. The typical process includes:
Heating: Steel billets are heated to a high temperature to achieve good plasticity and ductility.
Forming: The heated steel is processed via hot rolling, extrusion, or hot expansion to achieve the desired shape and size.
Cooling: Pipes are cooled naturally or with controlled cooling to achieve required mechanical properties.
Straightening and Cutting: Pipes are straightened and cut to standard lengths.
Features and Advantages:
Uniform internal structure with fewer defects, providing excellent mechanical properties.
Suitable for thicker walls and larger sections with higher load-bearing capacity.
Enhanced toughness and impact resistance due to heat treatment.
Ideal for heavy-duty and demanding structural applications.
Limitations:
Complex production equipment and higher energy consumption, resulting in higher manufacturing costs.
Dimensional accuracy and surface finish are generally lower than cold-formed pipes and may require further processing.
Longer production cycle.
Mechanical Properties and Result Stability Comparison
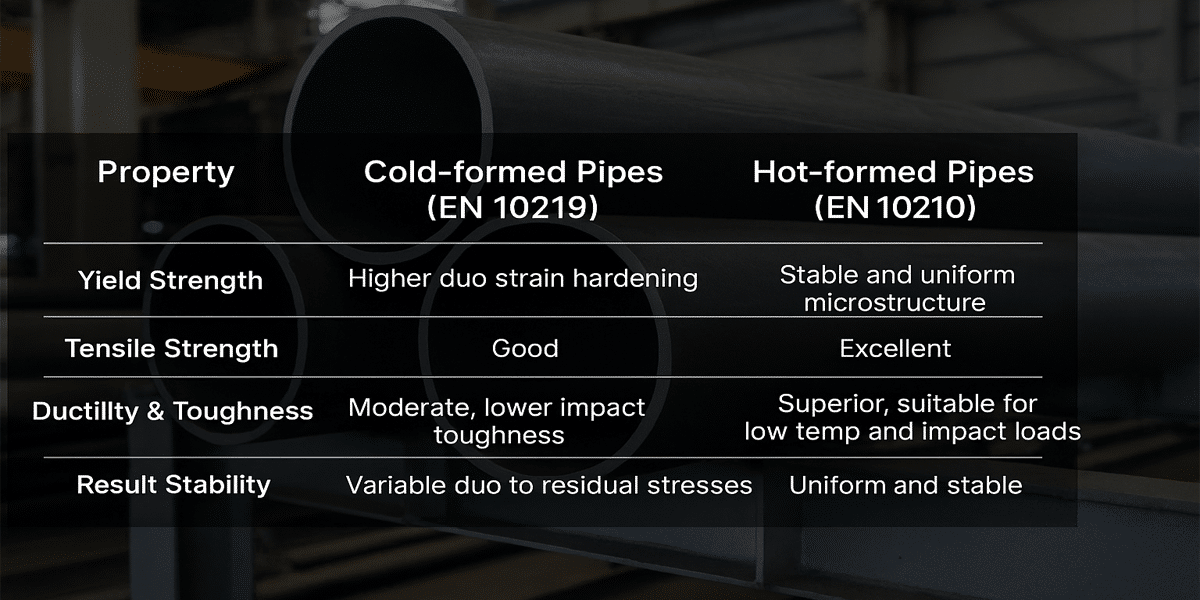
1. Cold-formed Steel Pipes (EN 10219)
Yield Strength
During the cold-forming process, the steel undergoes plastic deformation, resulting in strain hardening that typically leads to higher yield strength. This makes cold-formed pipes suitable for light to medium load-bearing applications.
Tensile Strength
Cold-formed pipes generally have good tensile strength; however, due to cold working, their ductility and toughness may be somewhat reduced, especially under low-temperature or impact loading conditions.
Ductility & Toughness
Compared to hot-formed pipes, cold-formed pipes exhibit lower ductility and impact toughness, making them more susceptible to cracking or brittle fracture due to internal stress concentration.
Performance Uniformity and Stability
Cold forming can introduce residual and processing stresses, which may cause some variability in material performance. Proper heat treatment or stress-relief processes after manufacturing can improve stability.
2. Hot-formed Steel Pipes (EN 10210)
Yield Strength
Hot forming refines the steel’s grain structure and produces a uniform internal microstructure, resulting in stable and consistent yield strength.
Tensile Strength
The hot-forming process enhances plasticity and ductility, giving the pipes excellent tensile strength and toughness suitable for complex stress conditions.
Ductility & Toughness
Hot-formed pipes have superior toughness, particularly under low-temperature and impact load scenarios, with high resistance to cracking and impact damage.
Performance Uniformity and Stability
Due to uniform heating and controlled forming, hot-formed pipes have a stable and uniform mechanical performance, making them ideal for applications requiring strict structural safety.
Typical Application Scenarios Analysis
1. Typical Applications of EN 10219 Cold-formed Steel Pipes
Due to their high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface, and relatively high yield strength, cold-formed steel pipes are widely used in light to medium load structural and mechanical manufacturing fields. Typical applications include:
Building Structures
Used in light steel frames, curtain walls, stair railings, and other architectural components, benefiting from precise dimensions that facilitate installation and enhance aesthetics.
Mechanical Manufacturing
Commonly used as frames, supports, and conveyor equipment structures, valued for stability and ease of welding and machining.
Furniture and Interior Decoration
Applied in office furniture, shelving, and display racks, leveraging smooth surfaces and versatile shaping capabilities.
Light Transportation Equipment
Used in bicycle frames, auxiliary structures of automotive chassis, meeting requirements for lightweight design and strength.
Combining high precision with good mechanical properties, cold-formed steel pipes perform excellently under light to medium loads and are cost-effective for mass production.
2. Typical Applications of EN 10210 Hot-formed Steel Pipes
Thanks to their excellent toughness, high strength, and thicker walls, hot-formed steel pipes are suitable for heavy load and harsh working conditions. Typical application areas include:
Large-scale Buildings and Bridges
Used for main bridge beams, industrial plant supports, and large-span roof trusses, providing high load capacity and toughness to ensure structural safety.
Petrochemical Equipment
Applied in high-pressure vessels, pipe supports, and tower structures, capable of withstanding complex loads and harsh environments.
Heavy Machinery and Equipment
Used as load-bearing structures in cranes, mining machinery, and construction equipment, meeting strength and durability requirements.
Transportation Infrastructure
Employed in rail transit, port machinery, and major vehicle components, capable of bearing high impact loads.
Summary of Advantages: Hot-formed steel pipes possess excellent impact toughness and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term stable performance under severe conditions, ideal for heavy-duty and high-safety engineering projects.
Steel Pipe Selection Guide: Project-Driven Decision Making
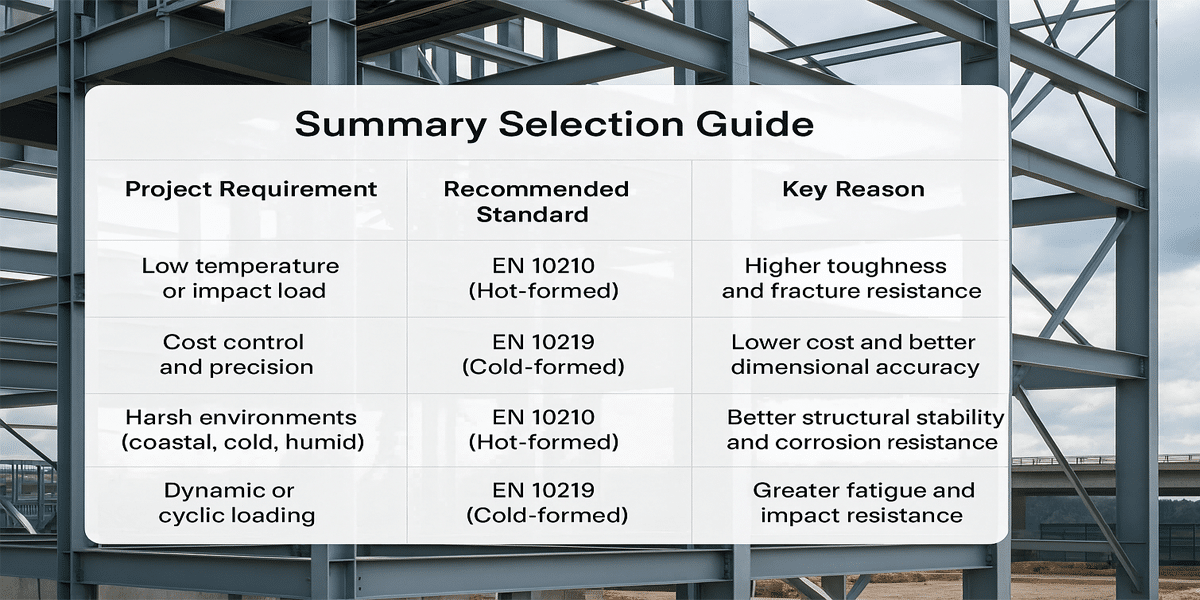
When choosing between EN 10219 (cold-formed steel pipes) and EN 10210 (hot-formed steel pipes), the key question is not “which one is better,” but rather “which one is more suitable” for your specific project. The following guide addresses five common project conditions to help you make a smart and efficient selection.
1. Will the project be exposed to low temperatures or impact loads?
✔ Yes → Choose EN 10210 (Hot-formed)
Hot-formed pipes offer excellent impact resistance and ductility, making them ideal for cold climates, seismic structures, and dynamic load conditions. Cold-formed pipes may have residual stress from forming, reducing toughness.
2. Is cost efficiency and dimensional precision a priority?
✔ Yes → Choose EN 10219 (Cold-formed)
Cold-formed pipes feature tighter dimensional tolerances and cleaner surfaces. They are suitable for standardized, mass production needs and provide better cost-performance for moderate load applications.
3. Is the project located in a harsh environment (e.g., coastal areas, high humidity, or freezing temperatures)?
✔ Yes → Choose EN 10210 (Hot-formed)
Hot-formed pipes, with more uniform microstructure and lower internal stress, offer better long-term performance in corrosive and fluctuating environments.
4. Will the structure be subject to repeated or dynamic loading?
✔ Yes → EN 10210 (Hot-formed) is the safer choice
Hot-formed pipes provide superior fatigue resistance and impact durability, essential for bridges, towers, cranes, and transport systems under cyclic or shock loads.
5. Does the project aim for lightweight, aesthetically pleasing structures?
✔ Yes → EN 10219 (Cold-formed) is more suitable
With clean appearance, smooth surface, and consistent geometry, cold-formed pipes are ideal for architectural design, interior structures, and visually exposed frameworks.
EN 10219 and EN 10210 steel pipes each serve different structural needs. If your project prioritizes cost-effectiveness and precision, cold-formed (EN 10219) is ideal. If your structure requires impact resistance or operates in harsh environments, hot-formed (EN 10210) is the safer choice.
Choosing the right standard means choosing the right foundation for your project. For further technical consultation or product support, feel free to reach out to: HeBei LongMa Steel Pipe Manufacturing Co.,Ltd. Email: enquiry@ilongma.com. LongMa Steel — Precision Meets Strength!




