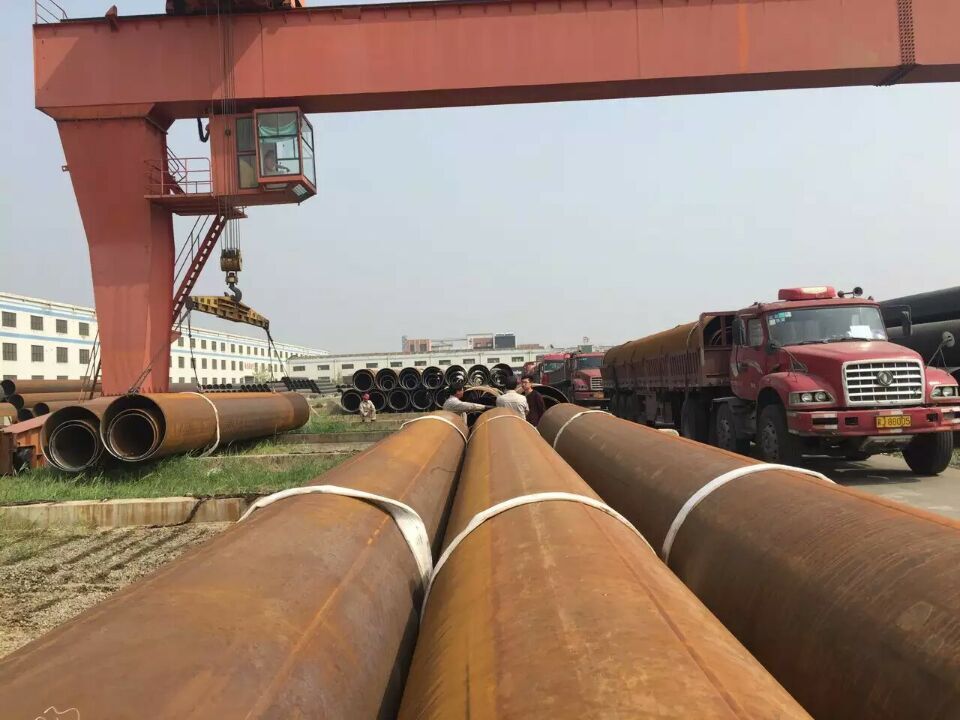
In modern construction and engineering fields, EN 10219 steel pipes have become one of the most widely used and reliable materials due to their excellent performance. Whether used as structural pipes for support or as essential load-bearing components, choosing the right steel pipe is crucial. However, with so many specifications and brands available in the market, making an informed purchasing decision to ensure that each pipe meets the project’s technical requirements and quality standards is a challenge that buyers must address. When purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes, it’s not just about price—what matters more are the technical parameters, material certificates, and applicable standards. Overlooking these key details can affect the stability and safety of the project. So, what should we focus on when purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes? This article will analyze the structural pipe technical requirements and key points to pay attention to during the procurement process, helping you make more precise decisions!
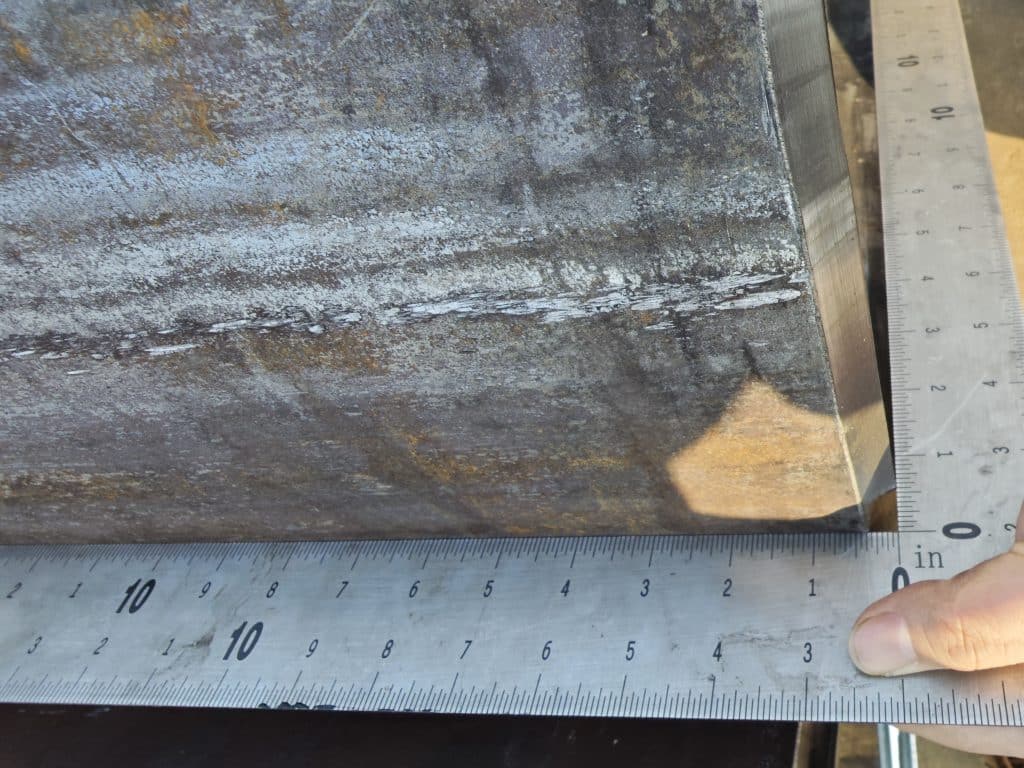

EN 10219 Standard Overview and Scope of Application
EN 10219 is a European standard that specifies the technical requirements for cold-formed welded steel pipes, particularly for use in construction and engineering structures. It outlines the material, dimensions, tolerances, mechanical properties, and other requirements for welded steel pipes. This standard applies to low-alloy or carbon steel pipes and is commonly used in structural, building, and piping applications.
1. Standard Overview
EN 10219 is divided into two parts:
EN 10219-1: This part covers the technical specifications for welded steel pipes, including pipe classification, requirements, and testing methods. It includes chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances.
EN 10219-2: This part provides specific dimensions, shapes, tolerances, weight, and inspection standards for steel pipes. It focuses on the technical requirements for manufacturing and testing.
This standard applies to cold-formed welded steel pipes used primarily in structural applications, offering high stability and load-bearing capacity. It not only covers basic specifications for steel pipes but also provides guidelines on surface treatment, corrosion resistance, heat treatment processes, and more.
2. Scope of Application
The EN 10219 standard is applicable to a wide range of engineering applications, including:
Building Structures: Such as supporting structures for steel frames, bridges, buildings, etc.
Civil Engineering: For large-scale projects like roads, railways, dams, etc.
Pipeline Systems: For oil and gas pipelines, water supply and drainage systems, and more.
Mechanical Structural Components: For equipment support frames, machine structures, and more.
The standard applies to cold-formed welded steel pipes, which are commonly used to manufacture large structures or frames, ensuring high stability and load-bearing capacity. It defines the conditions under which these pipes should perform in various demanding environments.
3. Material Requirements for Steel Pipes
EN 10219 specifies clear material requirements for steel pipes, typically categorized into:
Carbon structural steels such as S235, S275, S355, and other grades.
Alloy steels, which can be chosen for higher strength requirements.
The choice of materials ensures that the steel pipes meet the varying needs for strength and corrosion resistance in different applications.
4. Dimensions and Shape of Steel Pipes
The standard specifies requirements for the pipe’s dimensions, such as outer diameter, wall thickness, and length, and provides corresponding tolerance ranges. The dimensional specifications of EN 10219 ensure standardization of steel pipes, making it easier to integrate them with other structural elements.
Additionally, the standard considers different cross-sectional shapes (e.g., round, square) to meet the needs of various structural designs.
5. Mechanical Property Requirements
EN 10219 sets the mechanical properties that steel pipes must meet, typically including:
Tensile Strength: Steel pipes must achieve at least 355 MPa of tensile strength.
Yield Strength: Yield strength varies depending on the material grade, such as S235, which has a yield strength of 235 MPa.
Ductility and Impact Toughness: Steel pipes must also exhibit adequate ductility and impact toughness, especially for use in low-temperature environments.
6. Surface Treatment and Corrosion Resistance Requirements
For steel pipes exposed to external environments, EN 10219 specifies surface treatment requirements, such as anti-corrosion coatings or hot-dip galvanization, to enhance their corrosion resistance. The smoothness of the pipe surface is also an important consideration to ensure proper joining and use.
7. Inspection and Testing Requirements
According to EN 10219, manufacturers must conduct a series of inspections and tests, including:
Visual Inspection: Ensuring the pipes are free from visible defects.
Mechanical Property Testing: Including tensile strength, yield strength, and impact testing.
Dimensional and Tolerance Measurement: Verifying the pipe’s dimensions and wall thickness meet the specified tolerances.
Material Certification: Manufacturers must provide a material certificate verifying that the steel pipes meet the required chemical composition and mechanical properties.
8. Product Traceability and Certification
EN 10219 emphasizes product traceability and certification. Manufacturers must ensure that the quality of each batch of steel pipes can be traced, and they must provide corresponding material certificates to confirm that the pipes meet the required standards.

Key Technical Parameters to Consider When Purchasing EN 10219 Steel Pipes
When purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes, ensuring that the selected products meet project specifications is essential. Below are the key technical parameters that buyers should pay close attention to:
1. Material Grade and Composition
Material selection is one of the most critical factors. EN 10219 steel pipes are available in various strength grades such as S235, S275, and S355. Each grade is suited to different environments and load requirements. When purchasing, it’s important to verify the pipe’s chemical composition and request a valid material certificate to ensure compliance with your project’s technical needs—especially in terms of load-bearing and corrosion resistance.
2. Outer Diameter and Wall Thickness
The outer diameter and wall thickness of a pipe determine its load capacity, fit during installation, and structural stability. EN 10219 specifies strict dimensional requirements.
Outer Diameter: Critical for ensuring proper connection with other components.
Wall Thickness: Directly impacts the pipe’s strength and pressure resistance.
Always check that the dimensions align with the design requirements, including acceptable tolerance ranges.
3. Mechanical Properties (Tensile and Yield Strength)
The tensile strength and yield strength of the pipe are key indicators of its load-bearing capability. EN 10219 mandates minimum mechanical properties depending on the steel grade. For example, S235 typically has a yield strength of 235 MPa, while S355 offers 355 MPa. Verifying these values ensures structural safety and performance.
4. Impact Toughness and Ductility
In applications involving low temperatures or dynamic loads, the impact toughness and ductility of the pipe become critical. In such environments, using steel pipes with high toughness helps prevent brittle failure. Always confirm these properties if your project operates under extreme conditions.
5. Surface Quality and Treatment
The surface quality of the pipe affects its durability and corrosion resistance. Surface defects such as cracks, rust, or scale can compromise performance. In addition, surface treatments like hot-dip galvanizing or protective coatings can significantly extend service life. Ensure the pipe surface is smooth and defect-free, and choose an appropriate coating based on your environment.
6. Welding Quality
Since EN 10219 pipes are typically welded, the quality of the weld seam is crucial to structural integrity. Poor welding can be a major weak point. Request welding process reports and quality assurance documentation from suppliers to ensure the welds are strong, uniform, and free from defects.
7. Dimensional Tolerances
Tolerances in outer diameter, wall thickness, and length must conform to the EN 10219 specification to ensure proper fit and load distribution in structural assemblies.
Outer Diameter Tolerance: Ensures compatibility with joints and connections.
Wall Thickness Tolerance: Critical for uniform strength and performance.
Tight tolerances reduce installation issues and ensure consistent quality.
8. Inspection and Testing Requirements
EN 10219 mandates various inspection and testing procedures, including:
Mechanical Testing: To verify tensile strength, yield strength, and impact resistance.
Dimensional Checks: To confirm diameter, thickness, and length meet specifications.
Surface Inspection: To detect surface flaws.
Nondestructive Testing (NDT): Such as ultrasonic or X-ray testing to verify weld seam integrity.
Suppliers should provide complete test reports and material certificates to prove compliance with these standards.
9. Length and Transportation Requirements
The length of the pipe should align with on-site installation needs to minimize cutting and welding. Also, consider transport logistics—longer pipes may require special handling to avoid deformation or damage during transit.
10. Standards Compliance and Certification
Ensure that the pipes conform fully to EN 10219 and that the supplier can provide valid material certificates, quality inspection reports, and relevant compliance documentation. Certified pipes help reduce risk and guarantee that the product meets international safety and performance standards.

Detailed Guide on Communicating Procurement Parameters with Suppliers
When purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes, it is crucial to ensure that the selected products meet the project requirements and technical standards. Effective communication with suppliers is key to ensuring the quality, delivery times, and after-sales support meet expectations. Below is a detailed guide on what to consider when communicating procurement parameters, including whether to verify CE certification and EN 1090 execution capability, as well as whether to request third-party witness inspections, especially for large projects.
1. Ensure Compliance with EN 10219 Standards
Before procurement, clearly specify that the steel pipes must comply with the EN 10219 standard. This ensures that the pipes meet your project’s requirements in terms of material, dimensions, mechanical properties, surface treatment, etc. You should confirm with the supplier that their products fully adhere to this standard, particularly in the following areas:
Material Grade: Such as S235, S275, S355, ensuring compliance with chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Dimensions and Tolerances: Verify that the outer diameter, wall thickness, and length meet design specifications.
Surface Treatment: Confirm whether hot-dip galvanizing, painting, or other treatments are required.
Recommendation: Ask the supplier to provide a material certificate (such as EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 certificate) to prove compliance with the relevant technical standards.
2. Verify Supplier’s CE Certification and EN 1090 Execution Capability
In certain countries or regions, especially within the European Union, structural products, including steel pipes, must have CE certification. When purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes, it is important to verify whether the supplier holds CE certification and whether they are capable of executing EN 1090 standards, especially for construction and structural projects.
CE Certification: Ensures that the steel pipes meet the essential safety requirements for the European market.
EN 1090 Execution Capability: EN 1090 applies to the execution of steel and aluminum structures. If the project involves structural construction, it is crucial that the supplier holds EN 1090-1 certification, proving their ability to execute structural work.
If your project involves structural steel or construction, especially large-scale structural projects, it is recommended to request the supplier’s EN 1090 certification and relevant quality assurance documentation.
Recommendation: Request CE certification and EN 1090 certificates from the supplier, along with any associated quality management documents.
3. Request Third-Party Witness Inspections (For Large Projects)
For large projects, especially those related to public safety or complex engineering tasks, it is recommended to request third-party witness inspections. Third-party witness inspections can ensure that the products meet quality standards and compliance during the production process.
Third-Party Witness Inspections: This can ensure that the pipes are manufactured according to standards and include inspections of welding quality, mechanical properties, surface treatment, etc.
Inspection Content: Typically includes visual inspection of the pipes, dimensional measurements, mechanical testing, nondestructive testing (such as ultrasonic testing), and weld quality checks.
For high-risk or highly demanding projects, third-party inspections ensure both the quality of the pipes and increase the reliability and safety of the project.
Recommendation: Request a third-party inspection report, especially for product sampling or comprehensive inspection before acceptance to ensure compliance with design and quality requirements.
4. Technical Parameter Checklist and Communication
When communicating with suppliers, it is essential to prepare a detailed technical parameter checklist beforehand. This will ensure that both parties have a shared understanding of the procurement specifications, and it will help avoid potential technical disputes later on. Below are the key parameters to confirm with the supplier:
1. Standard Requirements
Clearly specify that the steel pipes must comply with the EN 10219 standard.
If other international standards are involved, ensure they are specified in the agreement.
2. Material Grade
Confirm the required material grade, such as S235, S275, or S355, and ensure the material meets the chemical composition and mechanical property requirements.
3. Dimension Requirements
Outer diameter, wall thickness, and length must be specified according to the design requirements. Make sure to clearly define the tolerances for outer diameter and wall thickness (e.g., outer diameter ±1%, wall thickness tolerance -10% / +10%).
Confirm whether the required pipe lengths are fixed (e.g., 6 meters) or random lengths.
4. Surface Treatment
Confirm if surface treatment is required, such as hot-dip galvanizing, painting, or black pipe, and specify the treatment requirements and corrosion resistance level (e.g., C3, C5 corrosion protection grade).
5. Welding Requirements
If the pipes are welded, clarify whether weld ultrasonic testing (UT) or other nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are required to ensure weld quality meets project specifications.
Ensure there are no defects in the welds and that the welded joints comply with relevant standards.
6. Mechanical Property Testing
Request the supplier to provide tensile strength, yield strength, and impact toughness test results, especially if the project involves low-temperature conditions (e.g., requiring low-temperature impact testing at -20°C).
7. Material Certificate
Request the supplier to provide EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 material certificates to verify that the steel pipes meet the required chemical composition and mechanical properties.
If additional certifications or independent inspection reports are required, ensure these are requested.
8. Third-Party Inspection Requirements
For large or high-demand projects, it is advisable to request third-party witness inspections conducted by independent organizations (such as TUV, SGS, DNV) to ensure the products’ quality and compliance.
Third-party inspections may include visual inspections, dimensional measurements, mechanical property tests, and nondestructive testing (NDT).
5. Confirm Delivery Times, Payment Terms, and After-Sales Support
Delivery Times: Ensure the supplier can deliver the pipes on time, especially for bulk orders. Confirm the production and shipping schedules.
Payment Terms: Agree on the payment method (e.g., Letter of Credit (LC) or Telegraphic Transfer (TT)).
After-Sales Support: Clarify the supplier’s responsibilities in case of quality issues, including return/exchange policies, warranties, and dispute resolution.
In conclusion, communicating procurement parameters for EN 10219 steel pipes with suppliers is crucial not just for confirming specs and prices, but also for ensuring product quality, delivery time, and after-sales support. By defining clear technical requirements, verifying compliance, reviewing certifications, and requesting third-party inspections, you can minimize risks and ensure smooth project execution. Whether it’s a small project or a large one, effective communication and preparation are key to successful procurement. Following the tips in this guide will help you work efficiently with suppliers and get high-quality, reliable results.
We hope this guide helps you make informed decisions when purchasing EN 10219 steel pipes. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out!