- 1. Why is A53 Often Preferred?
- 2. Wide Applicability to “Most Scenarios”
- 3. Mature Specification System, Compatible with Common Size Systems
- 4. Clear Quality & Testing Requirements, Controllable Risks
- 5. Types and Grades of A53
- 6. Key Chemical and Mechanical Properties (Typical Upper/Lower Limits)
- 7. Maximum Chemical Composition (%)
- 8. Mechanical Properties (Minimum Values)
- 9. How to Choose Between A53 and Related Standards?
- 10. Typical Supply and Construction Key Points (Checklist for Purchasers/Engineers)
- 11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 12. LONGMA: Making A53 Procurement Easier and More Reliable
- 13. References and Basis
ASTM A53 is a general-purpose standard for black steel pipes or hot-dip galvanized carbon steel pipes (available as seamless Type S or electric resistance welded (ERW) Type E). It covers a wide size range of NPS 1/8–26, suitable for mechanical and pressure applications, as well as general transportation scenarios such as steam, water, gas, and air. With clear specifications, wide availability, high cost-effectiveness, and weldable/threadable properties, it is often used as the “default option” in engineering procurement.
Why is A53 Often Preferred?
-
Wide Applicability to “Most Scenarios”
- Applications: Suitable for mechanical and pressure uses, as well as steam, water, gas, and air pipelines; compatible with processing such as welding, bending, and flanging.
- Surface & Anti-Corrosion: Optional black pipe or hot-dip galvanization (the standard specifies clear requirements for the average zinc coating weight of galvanized pipes).
- End Forms: Common end types such as PE (Plain End), BE (Beveled End), and TH (Threaded End) are available, facilitating quick matching with valves and fittings.
-
Mature Specification System, Compatible with Common Size Systems
- Supplied according to NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) / Schedule (Wall Thickness Schedule), making it easy to match with dimension tables such as ASME B36.10M. Common schedules including SCH 10/40/80/160/XXS are fully covered.
- Common engineering practices such as threading, painting/galvanization have clear implementation guidelines in A53, minimizing resistance in procurement and construction.
-
Clear Quality & Testing Requirements, Controllable Risks
- Hydrostatic Test: Specifies minimum water pressure values for different ends (2500 psi for NPS ≤ 3, 2800 psi for NPS > 3) with a pressure holding time of not less than 5 seconds.
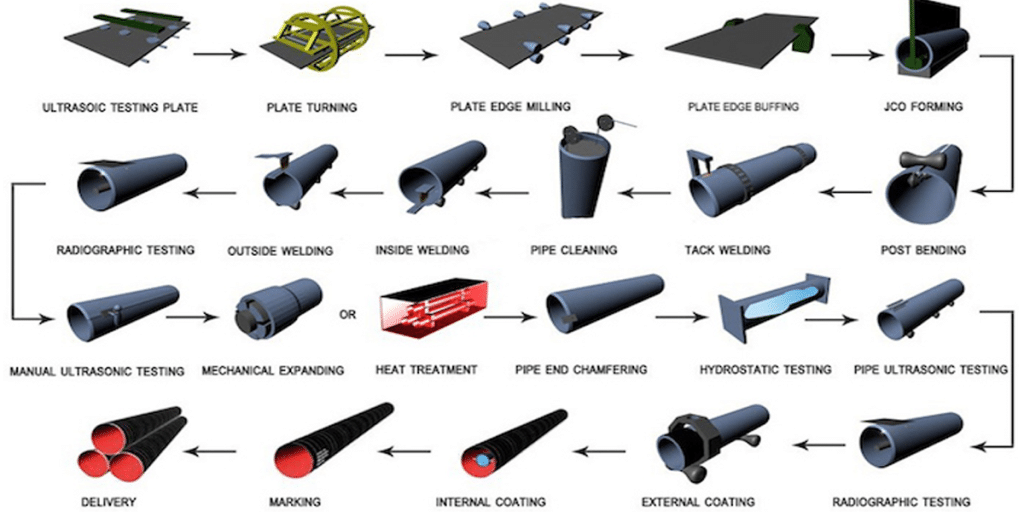
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Includes provisions for electrical testing/NDT of Type E (ERW) welds to ensure weld integrity.
Types and Grades of A53
ASTM A53 classifies products into three types and two grades:
- Type S: Seamless (Grades A, B)
- Type E: Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) (Grades A, B)
- Type F: Furnace Welded/Continuous Welded (Rarely used; not suitable for flanging)
Among them, Grade B has higher strength than Grade A and is more commonly used in engineering.
Key Chemical and Mechanical Properties (Typical Upper/Lower Limits)
Note: Minor differences may exist between different manufacturing methods and revised versions of the standard. The table below lists typical values commonly used in the industry; procurement shall be based on the contractual version of the standard and Material Test Certificate (MTC).
-
Maximum Chemical Composition (%)
| Item | Grade A | Grade B |
| C (Carbon)* | 0.25 | 0.30 |
| Mn (Manganese) | 0.95 | 1.20 |
| P (Phosphorus) | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| S (Sulfur) | 0.045 | 0.045 |
Note: The above are common limits for Type S/E; common auxiliary limits are Cu, Ni, Cr ≤ 0.40% and Mo ≤ 0.15%.
-
Mechanical Properties (Minimum Values)
| Indicator | Grade A | Grade B |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 330 | 415 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 205 | 240 |
(Original unit: ksi, corresponding to 48/30 for Grade A and 60/35 for Grade B)
How to Choose Between A53 and Related Standards?
- ASTM A106 (Seamless): The two have similar chemical compositions and applications, but A106 must be seamless and is more oriented towards medium-to-high temperature services. A53, however, can be seamless or ERW and is mostly used for normal/medium-to-low temperature and civil pipelines. For high-temperature applications or scenarios requiring seamless pipes, A106 is preferred.
- ASTM A500 (Structural Pipe): For structural load-bearing components, A500 is more commonly used in engineering; for medium transportation and general pipelines, A53 is preferred.
- API 5L (Line Pipe): API 5L is selected for long-distance oil and gas transportation or scenarios requiring PSL (Product Specification Level) systems; A53 is more economical for general on-plant or building mechanical and electrical pipelines. Extended Reading: Overview of API 5L
Typical Supply and Construction Key Points (Checklist for Purchasers/Engineers)
- Specify Type/Grade: The conventional option is A53 Type E / Grade B (ERW, with higher strength).
- Size and Wall Thickness: Specified by NPS & Schedule, e.g., NPS 2″ / SCH 40.
- Ends: Requirements for PE/BE/TH and thread standard (e.g., ASME B1.20.1).
- Surface/Anti-Corrosion: Black pipe, hot-dip galvanization (pay attention to zinc coating weight indicators), or external anti-corrosion primer.
- Testing: Whether hydrostatic/eddy current/ultrasonic testing is required; note the minimum water pressure and pressure holding time.
- Documents: Request MTC (EN 10204 3.1), dimension/appearance inspection records, etc., from the supplier.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can A53 be used for high temperatures?
A1: A53 can be used for general temperature conditions; for significantly high temperatures or scenarios requiring seamless pipes, A106 is more commonly specified in engineering.
Q2: Does the “preferred” status of A53 mean it can be used in all scenarios?
A2: No. The final selection depends on pressure rating, temperature, medium corrosiveness, etc. A53 is widely used because of its broad coverage and cost-effectiveness. For long-distance transportation, PSL certification, or specific material grades, API 5L or other standards should be considered.
LONGMA: Making A53 Procurement Easier and More Reliable
As a manufacturer specializing in round pipes, LONGMA has over 20 years of industry experience and has long provided A53 Type E (ERW) pipes and supporting services for building mechanical and electrical systems, equipment piping, and industrial medium transportation.
- Manufacturing Advantages: High-frequency ERW continuous production lines, post-weld heat treatment, and online/offline NDE (eddy current/ultrasonic testing) ensure stable weld quality.
- Quality Control: Full-size hydrostatic testing capability, as well as random inspections of dimensions, appearance, and galvanized coating thickness; EN 10204 3.1 MTC and traceable markings are provided with outgoing products.
- Engineering Adaptability: Supplies the full range of products according to NPS/Schedule, with optional PE/BE/TH ends and available black pipes/hot-dip galvanized pipes; also supports project-specific services such as cutting, beveling, and marking.
- One-Stop Selection: For projects requiring seamless pipes or large-diameter structural/line pipes, we can also provide product solutions complying with corresponding standards and offer comparative suggestions on A53 / A106 / structural pipes / line pipes to shorten decision-making time.
Contact us now with your drawings and specifications to receive a quotation and delivery plan within 48 hours:
References and Basis
- Application of A53, key points of hot-dip galvanization and hydrostatic test clauses: Specification interpretation and hydrostatic clause summary by Totten Tubes.
- Typical chemical and mechanical values (Grade A/B): Data sheets by American Piping; specification PDF by Octalsteel.
- Definition of Type/Grade and usage restrictions of Type F: Wikipedia entries and industry materials.
- Core differences between A53 and A106 (whether seamless is mandatory, applicable temperature range): Comparative interpretation and industry explanations by American Piping.