- 1. What is 3PE Coated Steel Pipe?
- 2. Corrosion Challenges of Steel Pipes in Marine Environments
- 3. Advantages of 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
- 4. Typical Application Scenarios: 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
- 5. Selection and Construction Considerations for 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
With the continuous expansion of global offshore resource development, marine engineering has become increasingly vital in areas such as oil and gas transportation, subsea pipeline construction, and offshore platform installation. In these harsh and corrosive marine environments, the durability and corrosion resistance of steel pipes are crucial to ensuring the success and longevity of engineering projects. Among the many anti-corrosion solutions available today, 3PE (Three-Layer Polyethylene) coated steel pipes stand out for their superior anti-corrosion performance, mechanical strength, and extended service life. This article explores the growing application of 3PE coated steel pipes in marine engineering, highlighting their technical advantages and market potential amid evolving industry demands.Let me know if you’d like this version tailored for a specific company or product!

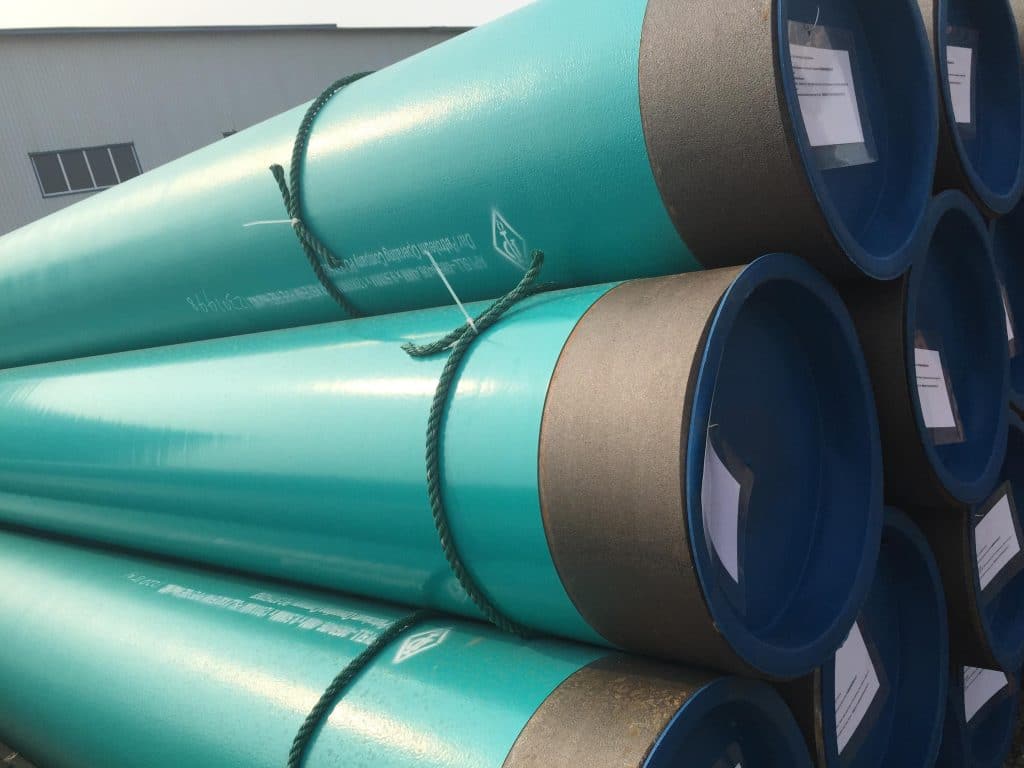
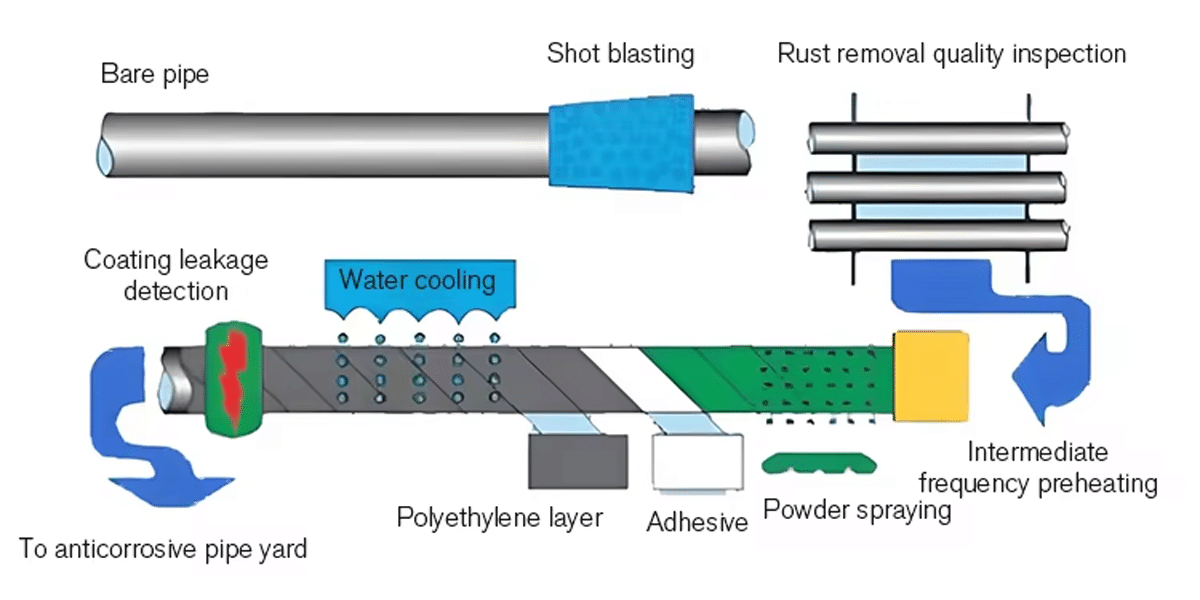
What is 3PE Coated Steel Pipe?
3PE (Three-Layer Polyethylene) coated steel pipe is a type of anti-corrosion steel pipe that features a three-layer external coating system. It is widely used in buried or submerged pipeline systems, especially in industries such as oil and gas transportation, water supply, and marine engineering.
The 3-layer structure includes:
Inner layer: Fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE): Provides excellent corrosion resistance and strong adhesion to the steel surface.
Middle layer: Copolymer adhesive: Acts as a bonding agent between the epoxy and polyethylene layers, ensuring a solid, uniform coating.
Outer layer: Polyethylene (PE) coating: Offers high mechanical strength and protection against external damage, moisture, and chemicals.
Key Advantages of 3PE Coated Steel Pipe:
1. Outstanding corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh environments such as saltwater, high humidity, and chemically aggressive soils;
2. Strong adhesion to the steel surface, reducing the risk of coating separation;
3. Excellent mechanical properties, including impact and abrasion resistance;
4. Long service life, typically exceeding 30 years under proper conditions;
5. High adaptability to extreme temperatures and complex installation conditions.
International Standards
DIN 30670 (Germany)
Title: Polyethylene coatings on steel pipes and fittings
This is one of the most widely referenced standards for 3-layer polyethylene (3PE) anti-corrosion coatings on steel pipes.
ISO 21809-1 (International Organization for Standardization)
Title: Petroleum and natural gas industries — External coatings for buried or submerged pipelines used in pipeline transportation systems — Part 1: Polyolefin coatings (3-layer PE and 3-layer PP)
This standard is commonly applied in oil and gas industries for pipelines with 3PE or 3PP coatings.
EN 10289 (European Standard)
Title: Steel tubes and fittings for onshore and offshore pipelines – External polyethylene coating
It covers the requirements for PE-coated steel pipes used in both onshore and offshore environments.
SY/T 0413-2002(Chinese National and Industry Satandards)
Title: Technical standard for three-layer polyethylene coating for buried steel pipelines
A widely used standard in China’s oil and gas industry for 3PE coating applications.
Corrosion Challenges of Steel Pipes in Marine Environments
Marine environments pose severe and complex corrosion challenges to steel pipes. The combination of high salinity, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and biological activity significantly accelerates material degradation. The key challenges include:
1. High Salinity and Humidity
Seawater contains high concentrations of chloride ions (Cl⁻), which are highly corrosive to steel;
High humidity levels accelerate electrochemical reactions, leading to faster corrosion;
Areas such as the splash zone and tidal zone experience particularly aggressive corrosion due to continuous wet-dry cycles.
2. Oxygen Concentration Cell Corrosion
Differences in oxygen availability at various depths or along the pipe surface create oxygen concentration cells;
These differences can lead to localized corrosion, including pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in submerged or partially buried pipelines.
3. Biofouling and Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC)
Marine organisms such as algae, barnacles, and bacteria attach to the pipe surface and form biofilms;
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB), in particular, can accelerate corrosion through biochemical reactions.
4. Temperature Fluctuations and UV Exposure
Coastal and offshore structures face significant day-night temperature shifts and tidal influences, which can cause protective coatings to crack or delaminate;
Ultraviolet radiation can also degrade exposed coatings over time, reducing their effectiveness.
5. Mechanical Erosion and Flow-Induced Corrosion
Suspended particles like sand in seawater cause continuous abrasion, weakening the pipe surface;
Strong currents, waves, and vibration lead to erosion-corrosion and may initiate microcracks or localized coating failures.
Advantages of 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
3PE (Three-Layer Polyethylene) coated steel pipes offer exceptional performance in marine environments, where corrosion, mechanical stress, and harsh conditions are constant threats. Their multilayer protective system makes them a preferred solution for offshore and coastal engineering projects.
1. Superior Corrosion Resistance
The fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) inner layer provides strong adhesion and excellent resistance to chemical and electrochemical corrosion, especially from chloride-rich seawater;
Ideal for submerged zones, splash zones, and tidal zones where corrosion is most aggressive.
2. Excellent Mechanical Protection
The outer polyethylene layer offers high resistance to abrasion, impact, and mechanical damage from seabed contact, underwater installations, or maintenance activities;
This reduces the risk of coating failure during transportation and installation.
3. Strong Adhesion and Long Service Life
The copolymer adhesive middle layer ensures a tight bond between epoxy and polyethylene, preventing delamination and water ingress;
Ensures a service life of over 30 years in demanding marine environments, minimizing maintenance costs.
4. Thermal Stability and Flexibility
Performs reliably under varying temperatures, from deep-sea cold to coastal heat;
Maintains flexibility to accommodate pipe movement caused by waves, tides, and currents.
5. Compatibility with Cathodic Protection Systems
3PE coatings work well in combination with cathodic protection, further enhancing corrosion control in offshore pipelines and structures.

Typical Application Scenarios: 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
Thanks to their outstanding anti-corrosion properties, mechanical strength, and long service life, 3PE coated steel pipes have been widely adopted in various marine engineering projects. Below are several typical application cases:
1. Subsea Oil and Gas Pipelines
Description: Used to transport oil and gas between offshore platforms and onshore terminals, often under deep-sea pressure and saline environments;
Advantage: 3PE coating ensures long-term corrosion protection and mechanical durability, even under shifting seabeds and strong currents.
2. Port and Harbor Water Systems
Description: Installed in port areas for industrial cooling water systems, seawater intake, and wastewater discharge;
Advantage: Excellent resistance to impact and corrosion, suitable for installations exposed to wave action and frequent handling.
3. Offshore Wind Power Infrastructure
Description: Used in offshore wind turbine foundations as internal or external conduits for cables and drainage systems;
Advantage: Durable under long-term marine exposure, supports low-maintenance, long-lifespan requirements for green energy projects.
4. Coastal City Drainage and Flood Control Systems
Description: Applied in large-scale drainage pipelines that discharge rainwater or seawater in flood-prone coastal zones;
Advantage: The 3PE layer provides high resistance to salt spray and chemical corrosion, ensuring system reliability over time.
5. Submarine Cable Protection Channels
Description: Acts as a protective conduit for submarine power or communication cables;
Advantage: The outer polyethylene layer resists sand abrasion and tidal scouring, while the adhesive layer prevents moisture ingress for complete sealing.
Selection and Construction Considerations for 3PE Coated Steel Pipes in Marine Engineering
3PE (Three-Layer Polyethylene) coated steel pipes are widely used in marine engineering due to their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical performance. However, to ensure long-term reliability and cost-efficiency, both pipe selection and on-site construction practices must be carefully planned and executed. Below are key considerations:
Selection Considerations
1. Match Coating Type to Environmental Conditions
For deep-sea applications, reinforced 3PE systems are recommended for enhanced impact and pressure resistance;
In splash zones or tidal areas, select coatings with superior UV resistance and weathering durability.
2. Compatibility Between Steel Substrate and Coating
Ensure the base steel pipe complies with relevant standards such as API 5L, ASTM A106, or GB/T 9711;
Surface preparation should reach at least Sa2.5 level (near-white blast cleaning) to ensure proper adhesion of the fusion bonded epoxy (FBE) layer.
3. Coating Thickness and Expected Service Life
Typical layer thicknesses:
FBE layer: 100–150 μm
Adhesive layer: 170–250 μm
Polyethylene outer layer: 2.0–3.0 mm
Coating thickness should be aligned with the expected lifespan of the project (e.g., 30 years) and the corrosion class of the environment.
4. Integration with Cathodic Protection Systems: For buried or long-term submerged pipelines, assess whether sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems are required for additional protection.
Construction Considerations
1. Handling and Transportation
Avoid direct contact or collisions between pipes; use rubber pads or soft slings for lifting;
Do not drag pipes on the ground to prevent coating scratches or delamination.
2. Field Joint Coating
Weld joints must be treated using field-applied joint protection systems such as heat-shrink sleeves, heat-shrinkable wraparound sleeves, or liquid epoxy coatings;
Ensure the joint coating system matches the corrosion resistance of the original 3PE layer.
3. Backfilling and Installation
During subsea burial or port foundation installation, avoid sharp stones or materials that can damage the coating;
Use neutral or soft materials as backfill to reduce external stress on the coating.
4. Inspection and Maintenance
Post-installation testing should include holiday detection (spark testing) and coating continuity checks;
For underwater pipelines, perform periodic inspections using ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) to monitor coating integrity.
As marine engineering projects face increasingly harsh environments and complex technical demands, the role of 3PE coated steel pipes becomes ever more critical. By combining superior corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and adaptability to marine conditions, 3PE pipes serve as a reliable solution for subsea pipelines, offshore structures, port facilities, and coastal infrastructure.However, the true performance of these pipes depends not only on product quality, but also on proper selection, careful transportation, professional installation, and thorough post-installation inspection. When these factors are fully considered and correctly executed, 3PE coated steel pipes can significantly extend the lifespan of marine pipelines, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure the long-term safety and stability of the entire engineering system.Choosing 3PE is not just a material decision—it’s a long-term investment in project durability and operational reliability.




