- 1. Standard Overview: Definition Scope of ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106
- 2. Manufacturing Process Comparison of ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106 Steel Pipes
- 3. Applicable Environments and Working Conditions
- 4. Pressure Resistance & Grade Classification Comparison
- 5. Inspection Requirements & Compliance Standards
- 6. Selection Guide & Engineering Application Reference
As the energy, chemical, and power industries continue to evolve rapidly, the selection of steel pipe standards for industrial applications has become increasingly critical. With growing attention to material performance and cost-effectiveness, choosing the right specification that fits specific working conditions is a common challenge for engineers and procurement professionals alike. Standards such as ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106 represent some of the most widely used options, each catering to different pressure levels, temperature environments, and structural demands. These standards differ not only in manufacturing processes but also in their applicable scenarios, strength grades, and corrosion resistance. As a result, conducting a comprehensive structural steel pipe standard comparison is no longer a theoretical exercise—it is essential for the successful execution of engineering projects. This article takes an industry-focused approach to examine these standards through case examples and technical analysis, aiming to provide practical guidance for informed decision-making in industrial pipeline selection.

Standard Overview: Definition Scope of ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106
1. ASTM A671: Electric-Fusion-Welded Steel Pipe (Welded + Heat Treated)
Standard Name: Standard Specification for Electric-Fusion-Welded Steel Pipe for Atmospheric and Lower Temperatures Scope of Definition: ASTM A671 covers carbon steel pipes manufactured by electric fusion welding (EFW). These pipes are primarily intended for pressure applications at atmospheric or lower temperatures. The pipes are made from plates (commonly conforming to ASTM A285, A516, etc.) through welding and heat treatment processes.
Application Features:
Suitable for low-temperature pressure piping systems in power plants and petrochemical industries
Typically used in environments with low or no corrosiveness requiring structural stability
Offers flexibility in size ranges, customizable according to project needs
Typical Applications:
Boiler water wall piping in thermal power plants
Low-temperature, high-pressure water and steam piping
Non-corrosive pipeline networks such as flue gas desulfurization or air-cooling systems in power plants
2. API 5L: Line Pipe for Oil and Gas Transmission
Standard Name: Specification for Line Pipe Scope of Definition: API 5L, published by the American Petroleum Institute, covers both seamless and welded steel pipes designed specifically for transporting oil, natural gas, water, and other liquids in pipeline systems onshore or offshore.
Grading System:
Product Specification Levels (PSL) divided into PSL1 and PSL2
PSL2 has more stringent requirements for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and nondestructive testing
Application Features:
Wide range of strength grades, commonly B, X42 to X80 and higher
Supports long-distance transportation, high pressure, and large diameter pipelines
Good weldability and corrosion resistance (often with external anti-corrosion coatings)
Typical Applications:
Long-distance crude oil and natural gas pipelines
Onshore/offshore oil and gas gathering systems
Connecting pipelines in storage and transportation facilities
3. ASTM A106: Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
Standard Name: Standard Specification for Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service Scope of Definition: ASTM A106 applies to seamless carbon steel pipes intended for high-temperature service. These pipes are widely used in welding, bending, and flanging applications in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and refining. Grade Classification:
Divided into Grade A, Grade B, and Grade C (Grade B is most commonly used)
Higher grades provide greater strength but may have reduced toughness and machinability
Application Features:
Excellent high-temperature resistance suitable for long-term service
Chemically stable, appropriate for steam, hot oil, and high-temperature gases
Seamless manufacturing ensures suitability for high-pressure and high-purity applications
Typical Applications:
Piping systems for petrochemical heaters and furnaces
Superheated steam and hot water piping in power plants
Pipeline connections for high-temperature heat transfer media
Manufacturing Process Comparison of ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106 Steel Pipes
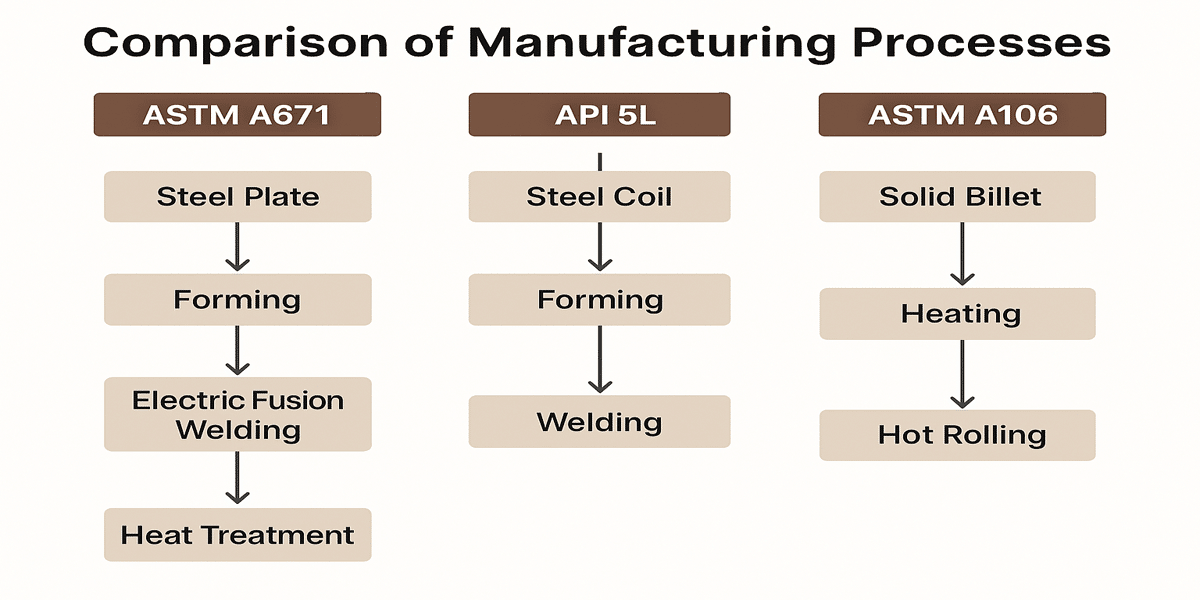
1. ASTM A671 Manufacturing Process
Plate Preparation: ASTM A671 pipes start from carbon steel plates, typically conforming to ASTM A285, A516, or similar standards.
Forming: Plates are formed into cylindrical shape using rollers.
Welding: Pipes are produced by Electric Fusion Welding (EFW), a high-frequency welding method that fuses the edges of the steel plate to form a longitudinal weld seam.
Heat Treatment: After welding, pipes undergo heat treatment (normalizing or tempering) to improve mechanical properties and reduce residual stresses.
Inspection: Non-destructive testing (NDT) including ultrasonic and hydrostatic tests ensure weld quality and pipe integrity.
2. API 5L Manufacturing Process
Raw Material: Both seamless and welded pipes are covered under API 5L.
Seamless Pipe Process:
Starts from a solid steel billet heated to high temperature.
The billet is pierced to form a hollow shell, then rolled or stretched to the desired diameter and wall thickness.
Pipes undergo heat treatment to achieve required strength and toughness.
Welded Pipe Process:
Steel coils or plates are formed into pipe shape.
Welding is usually done by Electric Resistance Welding (ERW) or Submerged Arc Welding (SAW).
Pipes may be heat treated depending on grade requirements.
Testing: API 5L demands rigorous mechanical testing and non-destructive testing (NDT) to ensure performance under pressure and corrosion resistance.
3. ASTM A106 Manufacturing Process
Seamless Pipe Only: ASTM A106 is exclusively for seamless carbon steel pipes.
Billet Heating: Steel billets are heated to high temperatures.
Piercing and Rolling: Heated billets are pierced to create hollow shells, then rolled and stretched to required sizes.
Heat Treatment: Some grades may require heat treatment for enhanced mechanical properties, but many pipes are supplied in as-rolled condition.
Finishing: Pipes are straightened, cut to length, and inspected for surface and dimensional quality.
Testing: Hydrostatic testing, tensile testing, and other NDT methods are applied to guarantee high-temperature serviceability.
Applicable Environments and Working Conditions
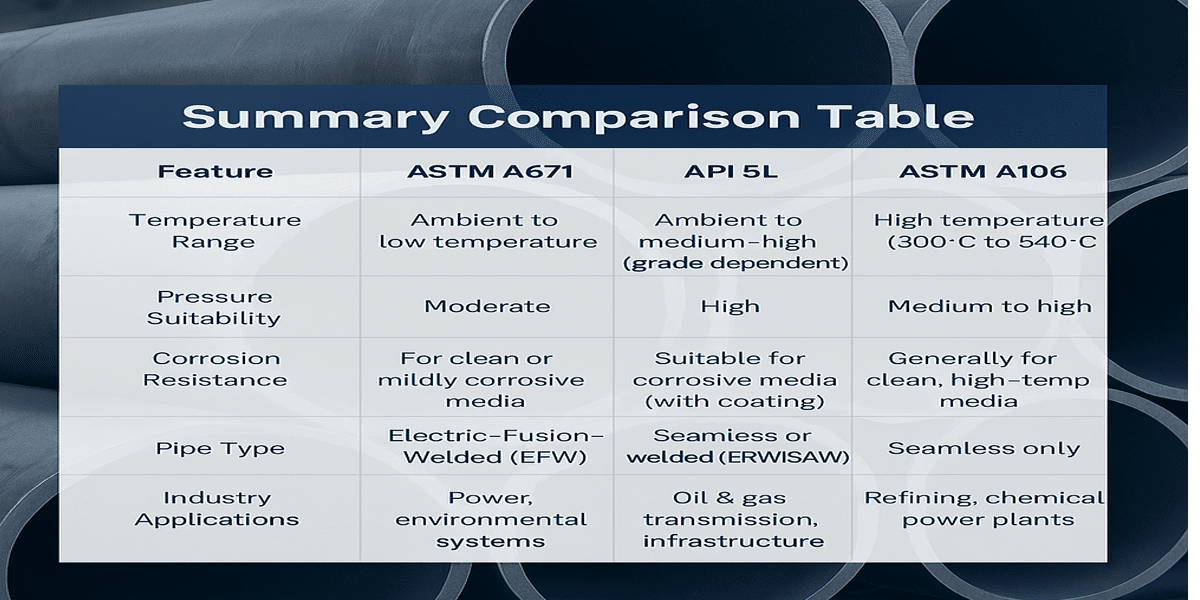
1. ASTM A671: For Moderate Pressure and Low/Atmospheric Temperature Applications
Working Environment:
Primarily used in systems operating at ambient or low temperatures (typically below 0°C).
Intended for non-corrosive or mildly corrosive environments.
Common in fixed installations rather than high-flow transport systems.
Operating Conditions:
Suitable for moderate pressure conditions (generally lower than API 5L line pipes).
Temperature resistance depends on the base plate material (e.g., ASTM A516 Gr.70).
Best suited for conveying steam, air, or clean water in low-corrosion settings.
Typical Applications:
Boiler water wall tubing in thermal power plants
Environmental protection systems (e.g., FGD/DeNOx piping)
Air-cooled systems, structural pipe supports
2. API 5L: For Long-Distance, High-Pressure, and Corrosive Environments
Working Environment:
Designed for long-distance transmission of oil, gas, and water, both onshore and offshore.
Handles a variety of corrosive fluids, including sour gas.
Often used with external anti-corrosion coatings, suitable for underground or subsea installation.
Operating Conditions:
Temperature: Ambient to medium-high, depending on material grade.
Pressure: Supports high-pressure applications (10–25 MPa or higher for X70/X80 grades).
Built for large-diameter, high-strength, and continuous-welded pipeline networks.
Typical Applications:
Cross-country natural gas transmission pipelines
Subsea oil & gas gathering systems
Crude oil transportation from field to refinery or terminal
3. ASTM A106: For High-Temperature, High-Pressure, and Clean Service Environments
Working Environment:
Specifically designed for high-temperature service (up to 540°C or higher).
Widely used in refineries, chemical plants, and power stations.
Suitable for clean or high-purity fluid transport (e.g., hydrogen, steam, thermal oil).
Operating Conditions:
Excellent performance under elevated temperatures (typically 300–540°C).
Good for medium to high pressure systems.
Seamless pipe structure allows for better handling of thermal expansion and pressure cycling.
Typical Applications:
Hydrogenation systems in refineries
Superheated steam lines in power plants
High-temperature heat exchanger inlet/outlet piping
Pressure Resistance & Grade Classification Comparison
1. ASTM A671 — EFW Welded Pipe (Pressure Depends on Base Plate & Weld Quality)
Pressure Performance:
ASTM A671 pipes are Electric Fusion Welded (EFW) and their pressure capacity largely depends on:
The strength of the steel plate used (e.g., A516 Gr.70);
Quality of the weld seam;
Pipe size (OD and wall thickness).
The base plate material determines tensile and yield strength, which governs the pressure limit.
Typically used for moderate pressure systems, around 2–6 MPa for steam or heat distribution lines.
Grade Examples:
A671 CC60 CL22 = A285 Grade C plate, Class 22 (heat treated)
A671 CC70 CL22 = A516 Grade 70 plate, Class 22 (higher strength)
2. API 5L — Line Pipe for Oil & Gas Transmission (Wide Strength Range)
Pressure Performance:
API 5L provides a comprehensive grade system (Grade B to X120), with increasing yield and tensile strengths.
Divided into two specification levels:
PSL1: Basic requirements for general pipeline use;
PSL2: Enhanced chemical, mechanical, toughness, and testing requirements.
Higher grades like X70 or X80 offer superior pressure resistance, suitable for:
High-pressure gas transmission;
Long-distance pipelines across challenging terrains.
3. ASTM A106 — Seamless Pipe for High-Temperature Service (Fixed Grade Options)
Pressure Performance:
ASTM A106 covers seamless carbon steel pipes, ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Comes in Grade A, B, and C, with increasing strength and decreasing ductility.
Pressure tolerance is also temperature-dependent, and design pressures must align with ASME B31.1 or B31.3 pressure-temperature tables.
Inspection Requirements & Compliance Standards
1. ASTM A671 – Electric Fusion Welded Steel Pipe
Compliance Scope:
Designed for pressure service, suitable for moderate or low-temperature conditions;
The standard emphasizes consistency and integrity between the base plate (e.g., A516) and the welded joint.
Inspection Requirements:
Visual Inspection: To assess the weld seam surface quality;
Radiographic Testing (RT): Full or spot radiography of welds;
Class numbers (e.g., Class 10–42) reflect different combinations of heat treatment, impact test, and RT requirements;
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): For detecting internal flaws in welds or base material;
Flattening/Bending Tests: Assess ductility and structural integrity of the weld and pipe body;
Impact Testing: Required for low-temperature grades (e.g., −29°C or −46°C service);
Hydrostatic Test: 100% hydro test is mandatory for each pipe length.
Certification:
Supplied with a Mill Test Certificate (MTC);
Clearly states plate origin, grade, welding method, and all test results.
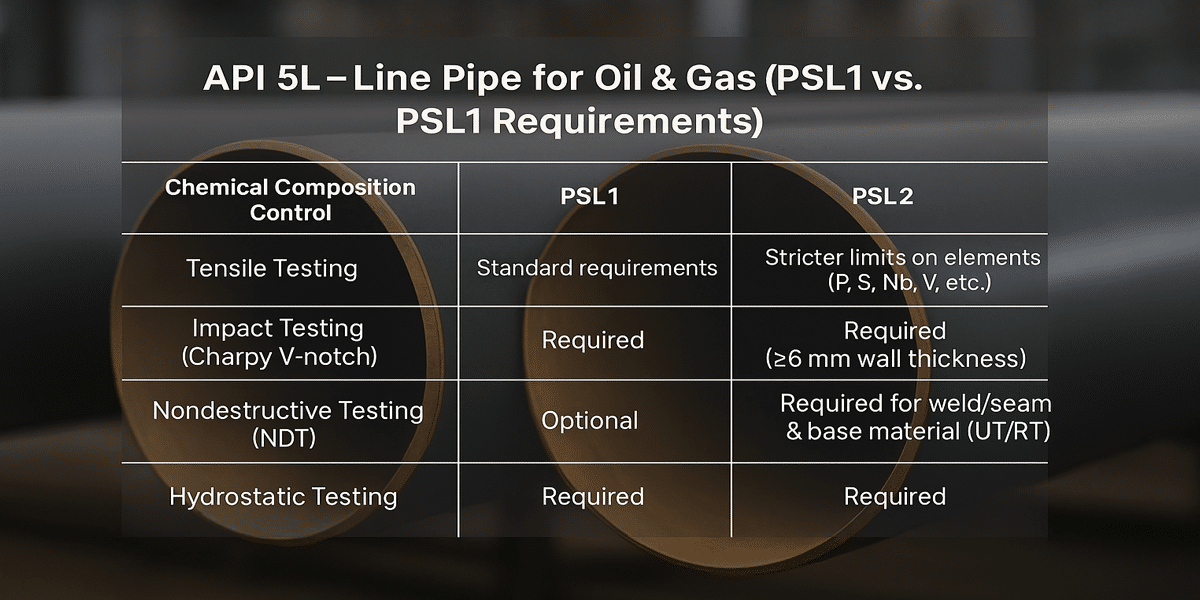
2. API 5L – Line Pipe for Oil & Gas (PSL1 vs. PSL2 Requirements)
Compliance Scope:
The primary standard for pipeline transport of oil and gas;
Split into two product specification levels:
PSL1: Basic quality requirements;
PSL2: Stricter chemical, mechanical, and testing requirements.
Inspection Requirements:
⚠️ PSL2 also requires manufacturing procedure consistency, traceability, and may include hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) resistance.
Certification:
Delivered with an API monogram and full MTC;
Clearly indicates grade, PSL level, manufacturing process (e.g., ERW, SAW), and test results.
3. ASTM A106 – Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High Temperature
Compliance Scope:
Designed for high-temperature and high-pressure industrial applications (e.g., power plants, refineries);
Seamless construction ensures high integrity and uniform performance.
Inspection Requirements:
Visual Inspection: Check for cracks, laps, scale, or surface defects;
Tensile Testing: Required for verifying mechanical properties;
Flattening Test: Tests ductility and wall stability;
Bending Test (optional): Verifies flexibility and resilience;
Hydrostatic Test: Mandatory for every pipe length;
Nondestructive Examination (NDE): Optional unless specified by the purchaser (refer to supplement sections like S/R series in the standard).
Certification:
Supplied with a Mill Test Certificate (EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2);
Includes full traceability: heat treatment status, chemical composition, mechanical tests.
Selection Guide & Engineering Application Reference
1. Key Selection Factors
Choosing between ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106 depends on multiple engineering and project-specific considerations:
Design pressure & temperature: High temperature → A106; High pressure, room temp → API 5L; Moderate → A671
Pipe construction method: Seamless preferred for high integrity (A106); welded acceptable in low-risk
Regulatory & code compliance: Project governed by ASME B31.1/31.3 → often A106; API pipelines → API 5L
Material availability & cost: A106 more expensive; A671 more flexible due to plate sourcing
Inspection & testing complexity: A671 (welded) needs more NDT; API 5L PSL2 strict; A106 seamless is simpler
Corrosion/environmental factors: API 5L PSL2 allows better control of impurities; special coatings may apply
2. ASTM A671 – Recommended Applications & Selection Notes
Best for:
Moderate-pressure systems (e.g., 2–6 MPa) at ambient or slightly elevated temperatures.
Thermal and process lines in power generation, chemical plants, and air cooling systems.
Where large-diameter, welded pipes are acceptable and radiographic weld inspection is feasible.
Selection Tip:
Choose Class 22 or higher if impact resistance or full RT is required.
The base plate material (e.g., A516 Gr.70) largely determines the strength and suitability.
Cost-effective for non-critical applications with good weld quality control.
3. API 5L – Recommended Applications & Selection Notes
Best for:
Oil & gas pipelines, both onshore and offshore;
Long-distance high-pressure transmission lines (including sour service if PSL2 or HIC resistant grades are used);
Projects requiring strict dimensional control, fracture toughness, and code compliance with ISO/CSA/EN equivalents.
Selection Tip:
Opt for PSL2 grades (X60, X70, X80) when:
Toughness and fracture resistance are essential;
Sour service or low temperature needs are present;
Consider Seamless (SMLS) or Submerged Arc Welded (SAW) depending on diameter, wall thickness, and pressure class.
4. ASTM A106 – Recommended Applications & Selection Notes
Best for:
High-temperature and high-pressure services, such as:
Boiler piping, superheaters;
Petrochemical processing lines;
Heat exchangers and steam lines in refineries.
Systems governed by ASME/ASTM piping codes requiring seamless pipe.
Selection Tip:
Grade B is most commonly used for industrial piping;
Grade C preferred for higher strength at elevated temperatures;
Seamless structure ensures better performance under thermal stress and cyclic loads.
Engineering Use Case Examples
Power Plant Steam Systems → ASTM A106 Gr.B/C (seamless, high-temp)
Natural Gas Pipeline (1000 km, X70) → API 5L PSL2 X70, SAWL
Condensate Return Lines → ASTM A671 CC70 Class 22
Offshore Oil Transport → API 5L X60+ PSL2 with NACE compliance
District Heating Networks → A671 for above-ground insulated piping
Choosing between ASTM A671, API 5L, and ASTM A106 depends on the pipeline’s operating conditions, regulatory requirements, and cost-performance balance. A106 is ideal for high-temperature, high-pressure environments; API 5L is the go-to for long-distance oil and gas transmission; and A671 offers a cost-effective solution for moderate-pressure, large-diameter applications. A clear understanding of their differences enables better engineering decisions, especially when comparing structural steel pipe standards or determining how to choose between ASTM A106 and A671 for pipelines. In today’s complex industrial landscape, informed selection is key to safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability!